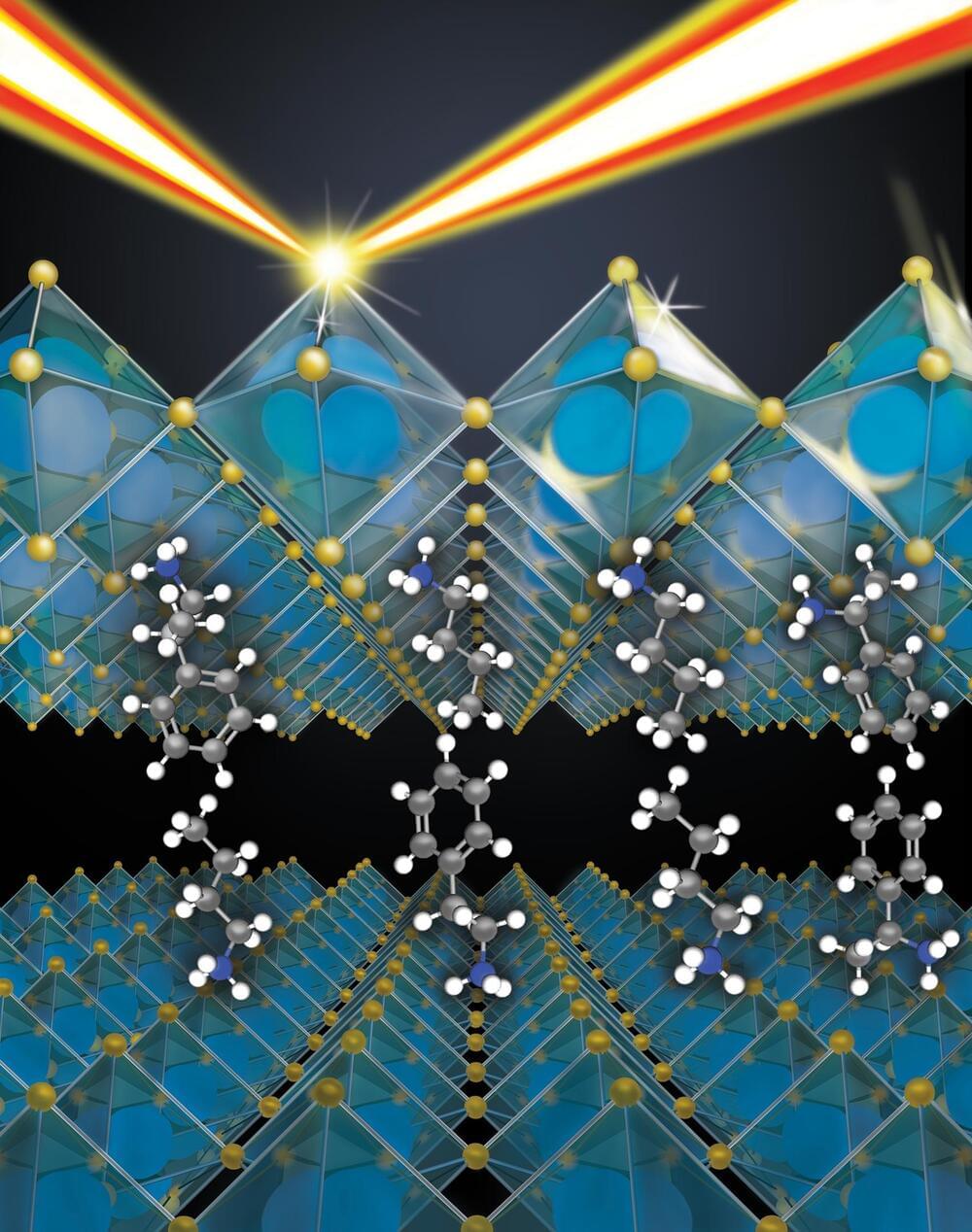
A research team has developed a novel “pulse-shaped” light method to enhance the electrical conductivity of PbS quantum dot solar cells. This new technique, which replaces the lengthy traditional heat treatment process, generates substantial energy at regular intervals, significantly improving efficiency and addressing defects caused by light, heat, and moisture exposure. PbS quantum dots, known for their wide absorption range and low processing costs, are now more viable for commercial use. This advancement is expected to facilitate the broader application of quantum dot technology in optoelectronic devices. Credit: SciTechDaily.com.
A research team headed by Professor Jongmin Choi from the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology has successfully developed a “PbS quantum dot” capable of quickly improving the electrical conductivity of solar cells. This collaborative effort involved Professor Changyong Lim of the Department of Energy Chemical Engineering at Kyungpook National University, led by President Wonhwa Hong, and Professor Jongchul Lim from the Department of Energy Engineering at Chungnam National University, under the leadership of President Jeongkyoum Kim.
The team identified a method to enhance electrical conductivity through the use of “pulse-shaped” light, which generates substantial energy in a concentrated manner at regular intervals. This method could replace the heat treatment process, which requires a significant amount of time to achieve the same result. This approach is expected to facilitate the production and commercialization of PbS quantum dot solar cells in the future.