Page 603
Jul 2, 2024
150-year-old conflict between Darwin and Wallace is resolved — by a machine
Posted by Dan Breeden in category: robotics/AI
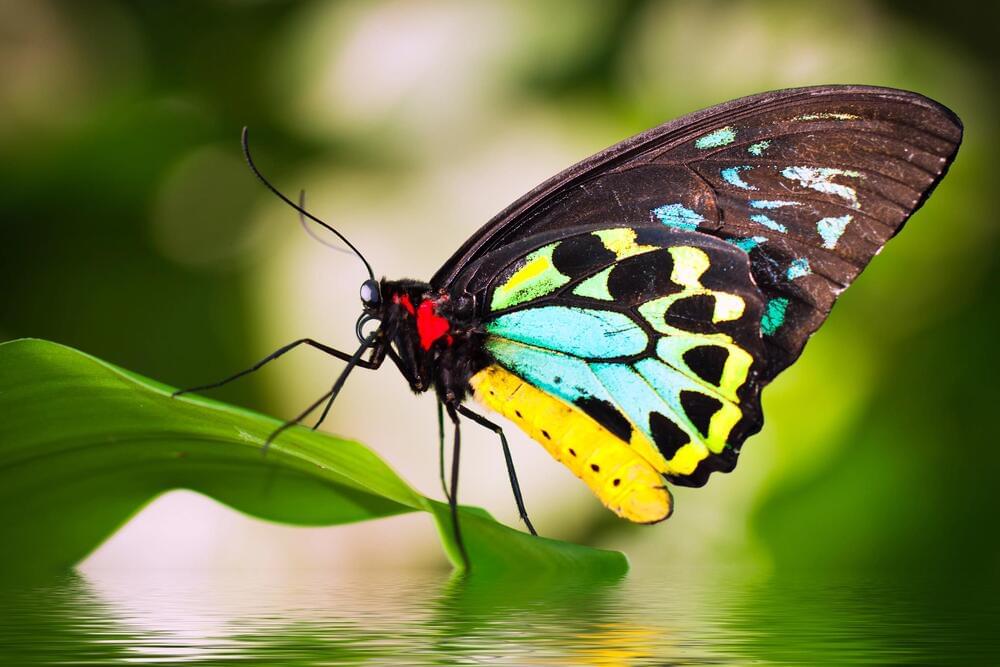
In the 1800s, a conflict between the founding fathers of evolution divided the community. Charles Darwin believed sexual selection drove the variation in butterfly colors and patterns of males, while contemporary rival Alfred Russel Wallace disagreed, predicting that broader natural selection played as important a role.
Darwin was adamant that sexual selection was not part of natural selection but solely related to differences in mating success. Natural selection covers a broader range of factors that contribute to an individual’s overall ‘fitness.’
In 2,024,150 years or so after these two iconic British evolutionary scientists began their heated rivalry over who was right, researchers have employed machine learning to settle the score. Scientists from the University of Essex, in collaboration with the Natural History Museum and AI research institute Cross Labs, Cross Compass, have used AI to analyze “sexual and interspecific variation” found across 16,734 dorsal and ventral images of birdwing butterflies.
Jul 2, 2024
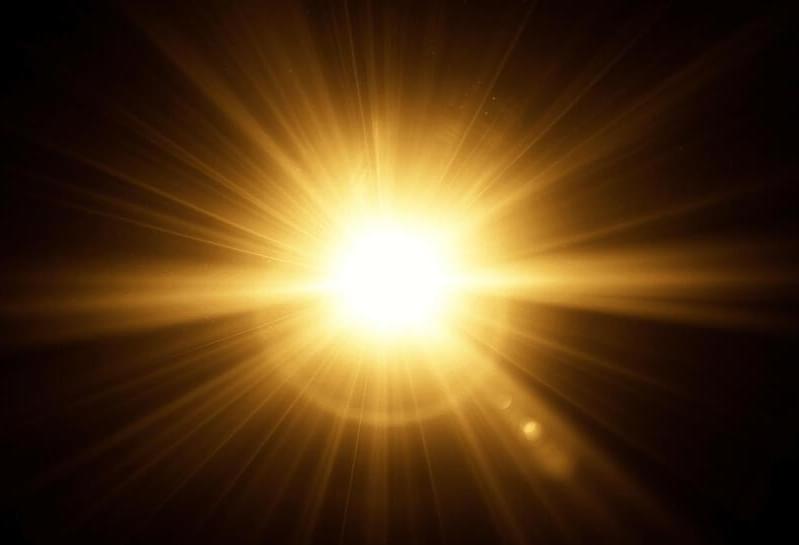
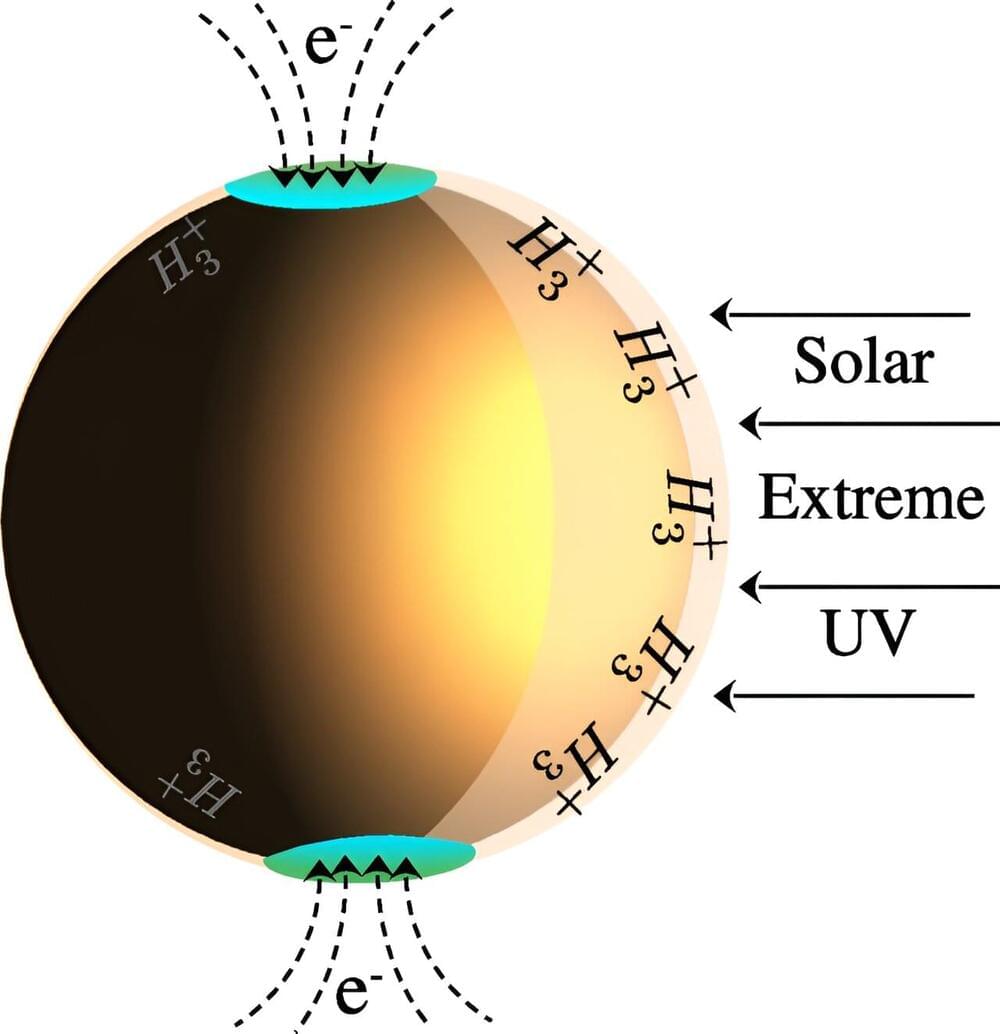
Infrared glow high in Jupiter’s atmosphere may be dark matter particles colliding
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: cosmology, particle physics
A pair of astrophysicists with Princeton University and the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory found possible evidence of dark matter particles colliding. In their study, published in Physical Review Letters, Carlos Blanco and Rebecca Leane conducted measurements of Jupiter’s equatorial region at night to minimize auroral influences.
Since it was first proposed back in the 1930s, dark matter has been at the forefront of physics research, though it has yet to be directly detected. Still, most in the field believe it makes up roughly 70% to 80% of all matter in the universe. It is believed to exist because it is the only explanation for odd gravitational effects observed in galaxy motion and the movement of stars.
Researchers posit that it might be possible to detect dark matter indirectly by identifying the heat or light emitted when particles of dark matter collide and destroy each other. In this new study, the researchers found what they believe may be such an instance—light in Jupiter’s dark-side outer atmosphere.
Jul 2, 2024
Scientists find desert moss ‘that can survive on Mars’
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: space
Moss that grows in Mojave desert and Antarctica may help establish life on the red planet, researchers say.
Jul 2, 2024
Giant Clams Are Models of Solar-Energy Efficiency
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: food, solar power, sustainability
A theoretical model for the illumination of photosynthesizing algae in giant clams suggests principles for high efficiency collection of sunlight.
Crops on a farm capture only about 3% of the available solar energy, much less than the 20%–25% captured by large solar arrays. Now a research team has used a theoretical model to explain efficiencies as high as 67% for photosynthesizing algae hosted by giant clams [1]. The researchers argue that clams achieve this performance with an optimized geometry. The mollusks may also adjust the algae clusters’ spacing according to changing light conditions. The researchers hope that an understanding of clams’ solar efficiency might help other scientists improve the efficiency of solar technology and explain aspects of the photosynthetic behavior of other ecosystems such as forests.
A photosynthetic cell can convert nearly every incoming photon to usable energy, says biophysicist Alison Sweeney of Yale University. But efficiency is much lower in larger systems such as agricultural fields. “Can we achieve near-perfect efficiencies over large land areas? This is an urgent question” as researchers try to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, Sweeney says.
Jul 2, 2024
Solar Power Investment Will Overtake Oil for the First Time Ever This Year
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, climatology, nuclear energy, sustainability
Year 2023 Basically solar will last several billion years and make type 0 civilization resources obsolete by making trillions of dollars in profits with nearly zero emissions.
Between the Covid-19 pandemic, the Ukraine conflict, inflation, and the renewables transition, the 2020s have been a volatile decade for energy. The pandemic reduced demand for electricity and oil all over the world, causing prices to plummet. Then the Ukraine invasion brought sanctions on Russian oil and gas, pushing energy prices up and leaving European countries scrambling (particularly for natural gas). High energy prices have since contributed to inflation, and in many places utility costs are far surpassing inflation. All the while, worry over climate change has continued to mount, with calls to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels growing ever louder.
In short, the energy situation in the US and around the world is a mess. But the International Energy Agency released some good news in its recent World Energy Investment report. The report is compiled annually, and the 2023 version came out at the end of May. For the first time ever, it found that investment in renewables—specifically solar power—will overtake spending on oil.
Continue reading “Solar Power Investment Will Overtake Oil for the First Time Ever This Year” »
Jul 2, 2024
Solar Power Generates Extreme Heat to Power Steel Furnace
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: solar power, sustainability
Scientists in Switzerland used solar energy to heat an object to over 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit that could potentially replace fossil fuels.
Jul 2, 2024
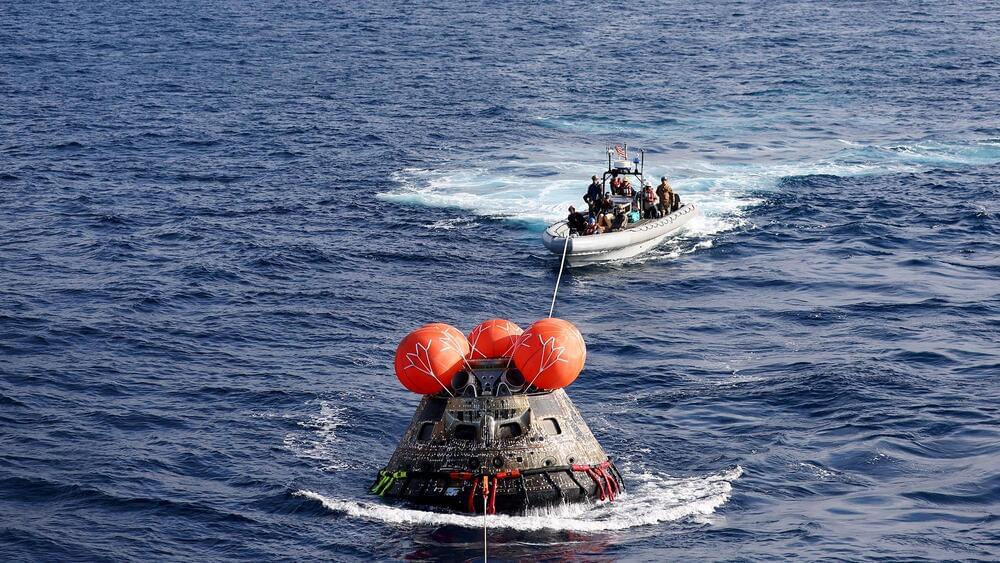
How NASA and SpaceX get spacecraft safely back on Earth
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: space travel
Water has a relatively low viscosity – that is, it deforms fast under stress – and it has a density much lower than hard rock. These two qualities make it ideal for landing spacecraft. But the other main reason water works so well is because it covers 70% of the planet’s surface, so the chances of hitting it are high when you’re falling from space.
The science behind splashdown is complex, as a long history proves.
In 1961, the U.S. conducted the first crewed splashdowns in history. These used Mercury reentry capsules.
Jul 2, 2024
Epstein-Barr Virus and Brain Cross-reactivity: Possible mechanism for Multiple Sclerosis detected
Posted by Natalie Chan in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
The role that Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) plays in the development of multiple sclerosis (MS) may be caused by a higher level of cross-reactivity, where the body’s immune system binds to the wrong target, than previously thought.
In a new study published in PLOS Pathogens, researchers looked at blood samples from people with MS, as well as healthy people infected with EBV and people recovering from glandular fever caused by recent EBV infection.
The study investigated how the immune system deals with EBV infection as part of worldwide efforts to understand how this common virus can lead to the development of multiple sclerosis, following 20 years of mounting evidence showing a link between the two.
Jul 2, 2024
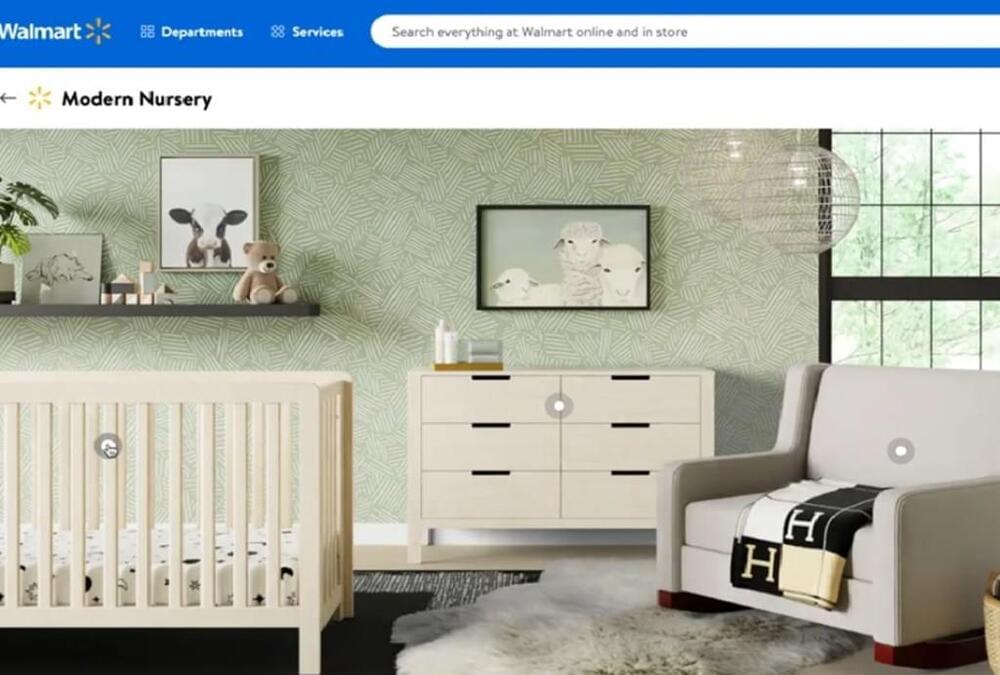
Walmart shows off its progress with augmented reality showrooms
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: augmented reality, robotics/AI
Walmart showed off its use of augmented reality and artificial intelligence in its retail operations. It turns out that AR is leading to better digital sales and cool new applications that haven’t been done before.
The techniques include virtual try-on of outfits, virtual showroom experiences and digital twins, said Desirée Gosby, vice president of emerging technology at Walmart Global Tech, in an interview with VentureBeat.
She emphasized the importance of AR and related technologies for enhancing customer experiences and improve productivity.