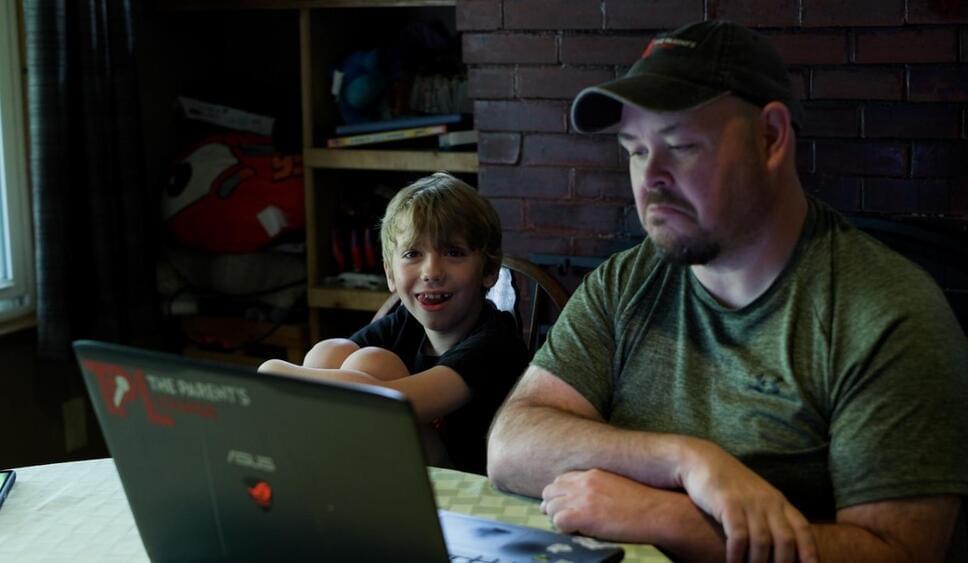
These advancements in AI technologies are happening in China despite the stringent measures that the U.S. is placing against its technological ambitions. The bans and embargoes on high-end chips Washington has placed on Beijing meant that Chinese companies have difficulty sourcing Nvidia’s latest, most potent AI processors. While China is hard at work trying to catch up on the hardware side of things, many experts believe it’s still at least a decade away from achieving parity with the United States.
It’s evident, though, that Chinese tech firms can catch up on the software side despite the hardware bans. Nevertheless, the White House wants to change that with a bill in the U.S. Congress that would give the American government more control over limiting the export of American AI code. Some parties are trying to limit the development of open-source AI tech to stop Chinese companies from using it, but doing so might do more harm than good for the U.S.
Clément Delangue, the CEO of Hugging Face, a firm that lets its users share its open-source AI projects, said, “Open-source AI is the foundation of AI development,” referring to how the collaboration of researchers and organizations in the U.S. allowed it to become the world leader in AI, “and it looks like China could do the same thing.”