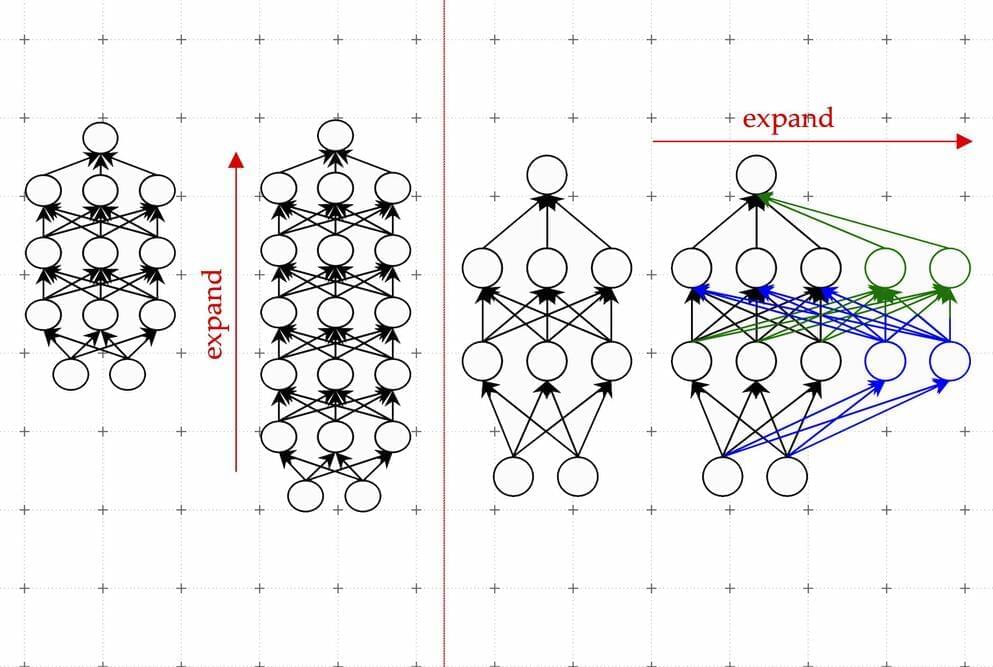
A team of researchers from the Université libre de Bruxelles and the French National Center for Scientific Research have shown for the first time that an exotic type of process violating causal inequalities can be realized with known physics. A violation of a causal inequality proves under theory-independent assumptions that certain variables in an experiment cannot be assigned a definite causal order.
This is a phenomenon that has been known to be possible in theory, but widely believed impossible in practice, at least in the known regimes of physics. The new study, published in Nature Communications, shows that such processes can in fact be realized in standard quantum mechanics using variables that are delocalized in time. The finding may have far-reaching implications for our understanding of causality in physics.
The concept of causality is essential for physics and for our understanding of the world in general. Usually, we think of events as happening in a well-defined causal order. That is, they are ordered according to some time parameter, such that events in the past can influence events in the future, but not vice versa. For instance, the sunrise causes the rooster to crow, but whether the rooster crows does not have any influence on the sunrise.