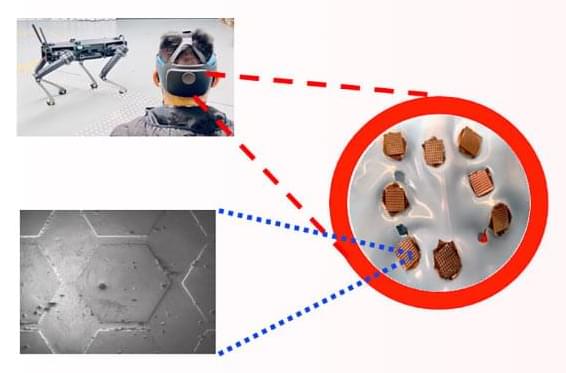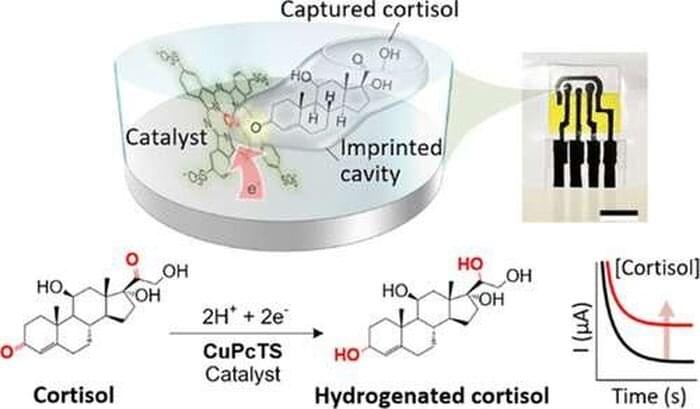
Researchers in the Oregon State University College of Engineering have developed a handheld sensor that tests perspiration for cortisol and provides results in eight minutes, a key advance in monitoring a hormone whose levels are a marker for many illnesses including various cancers.
Findings were published in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. The material and sensing mechanism in the new device could be easily engineered to detect other specific hormones, the researchers say—for example, progesterone, a key marker for women’s reproductive health and pregnancy outcomes.
“We took inspiration from the natural enzymes used in blood glucose meters sold at pharmacies,” said Larry Cheng, associate professor of electrical engineering and computer science. “In glucose meters, specific enzymes are applied to an electrode, where they can capture and react with glucose molecules to generate an electrical signal for detection. However, finding natural enzymes for cortisol detection is not straightforward, and natural enzymes are prone to instability and have a short lifespan.”