Feb 20, 2023
Designing advanced ‘BTS’ materials for temperature and long-wave infrared sensing
Posted by Jose Ruben Rodriguez Fuentes in categories: biological, health, robotics/AI, wearables
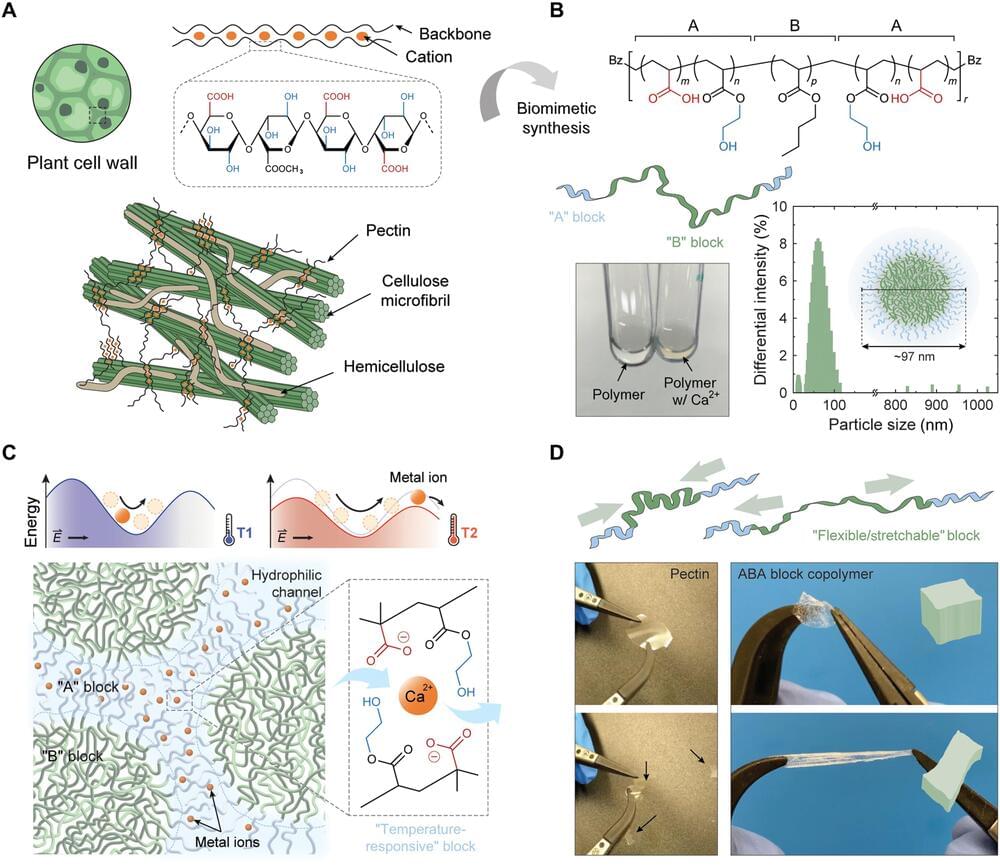
Materials scientists are often inspired by nature and therefore use biological compounds as cues to design advanced materials. It is possible to mimic the molecular structure and functional motifs in artificial materials to offer a blueprint for a variety of functions. In a new report in Science Advances, Tae Hyun Kim and a research team at the California Institute of Technology and the Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology in the U.S. and South Korea, created a flexible biomimetic thermal sensing polymer, abbreviated BTS, which they designed to mimic ion transport dynamics of pectin; a plant cell wall component.
The researchers used a versatile synthetic procedure and engineered the properties of the polymer to be elastic, flexible and stretchable in nature. The flexible polymer outperformed state-of-the-art temperature sensing materials such as vanadium oxide. Despite mechanical deformations, the thermal sensor-integrated material showed high sensitivity and stable functionality between 15° and 55° Celsius. The properties of the flexible BTS polymer made it well suited to map temperature variations across space-time and facilitate broadband infrared photodetection relevant for a variety of applications.
Organic electronic materials are competitive alternatives to conventional silicon-based microelectronics due to their cost-effective, multifunctional nature. Materials scientists seek to tailor the properties of such materials at the molecular level for a range of sensing applications for wearable and implantable devices with specific characteristics such as flexibility and elasticity. At present, there is an increasing demand for all-organic electronic devices to form a range of soft and active materials. For instance, organic thermal sensors are suited for remote health care and robotics, albeit with limitations.