Oct 6, 2023
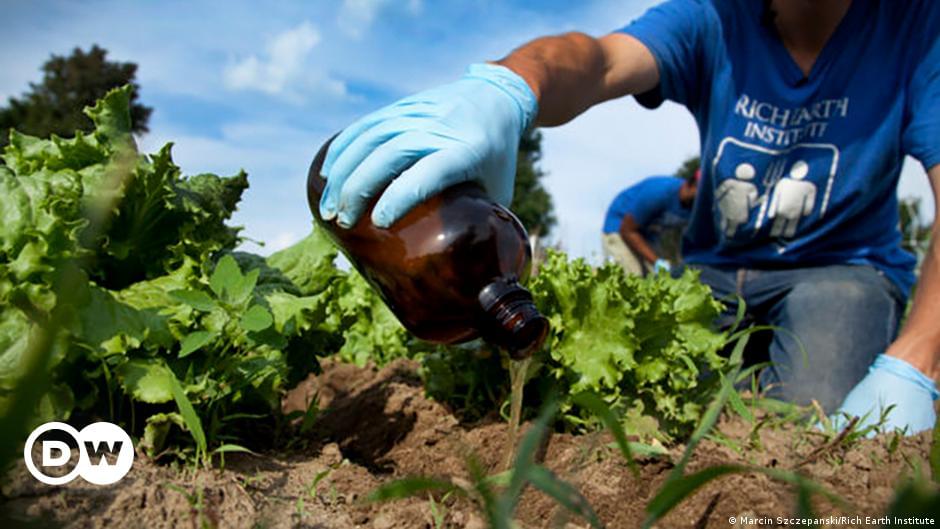
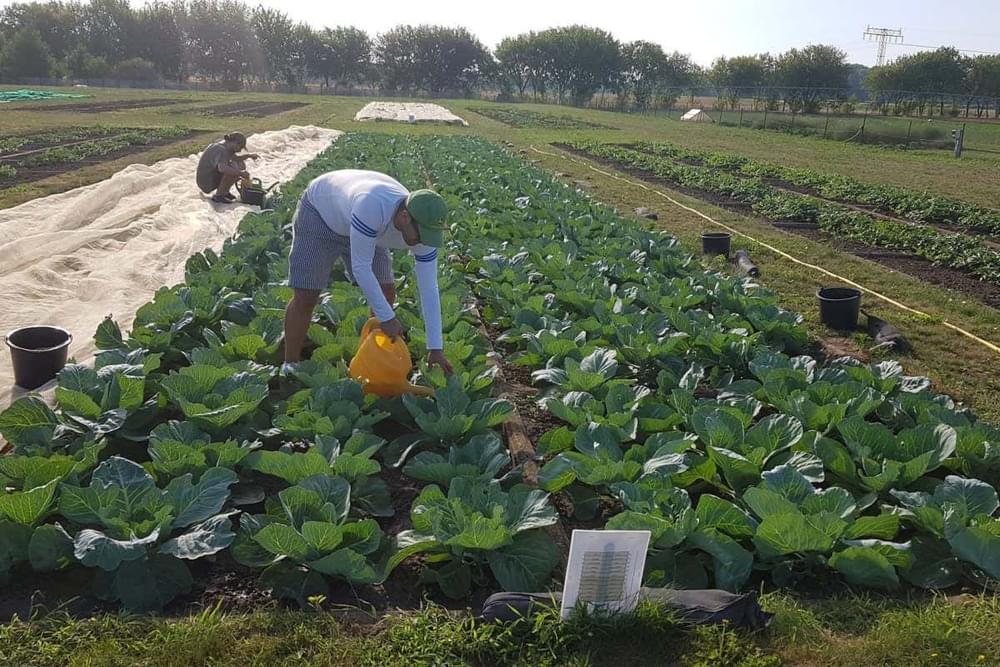
Recycling our poop to grow food more sustainably
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, food
My idea is that all the waste from human waste has vital things in it we could even someday have everything recycled back into its original form like if waste medicines or other nutrients could be extracted we could essentially recycle human waste having a near unlimited supply of chemicals which would be great for space traveling where nothing is wasted.
Poop’s got an image problem
And there’s also the issue of acceptance. Research suggests there are both cultural and psychological barriers standing in the way of wider bodily waste recycling.
Continue reading “Recycling our poop to grow food more sustainably” »