Another well-known method for physical learning is Equilibrium Propagation (EP), sharing similar procedure with coupled learning and being able to define the arbitrary differentiable loss function32. This method has been demonstrated in various physical systems, numerically in nonlinear resistor networks33 and coupled phase oscillators34, experimentally on Ising machines35.
So far, the MNNs based on the physical learning have been developed using the platform of origami structures28,36 and disordered networks29,37 to demonstrate machine learning through simulations. The experimental proposals involve using directed springs with variable stiffness38 and manually adjusting the rest length of springs31.
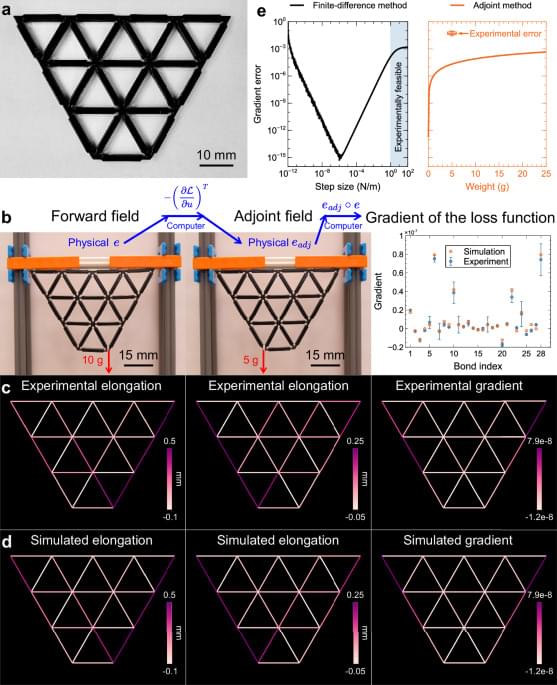
Here, we present a highly-efficient training protocol for MNNs through mechanical analogue of in situ backpropagation, derived from the adjoint variable method, in which theoretically the exact gradient can be obtained from only the local information. By using 3D-printed MNNs, we demonstrate the feasibility of obtaining the gradient of the loss function experimentally solely from the bond elongation of MNNs in only two steps, using local rules, with high accuracy. Besides, leveraging the obtained gradient, we showcase the successful training in simulations of a mechanical network for behaviors learning and various machine learning tasks, achieving high accuracy in both regression and Iris flower classification tasks. The trained MNNs are then validated both numerically and experimentally. In addition, we illustrate the retrainability of MNNs after switching tasks and damage, a feature that may inspire further inquiry into more robust and resilient design of MNNs.