Dec 13, 2024
Expanding momentum bandgaps in photonic time crystals through resonances
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: life extension, materials
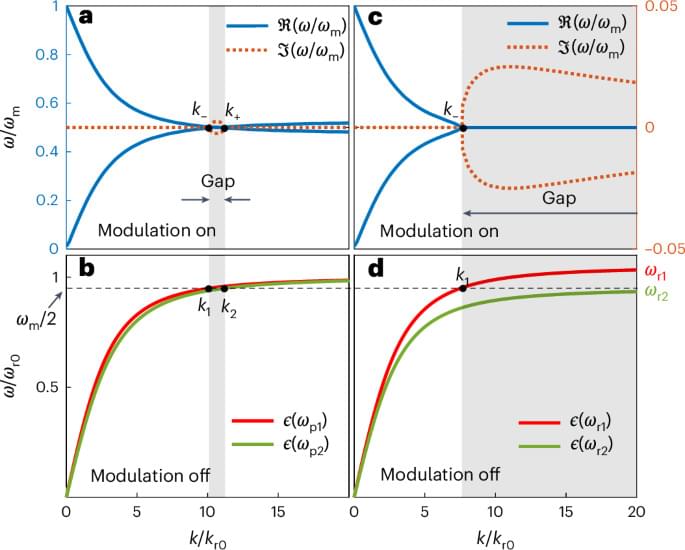
The size and strength of the momentum bandgap improve as the quality factor of the metasurface increases. Figure 3f shows that metasurfaces with a higher Q-factor provide wider momentum bandgaps for surface waves with larger amplification rates, assuming the same modulation function. In comparison, the metasurface discussed in Fig. 3b–e has a quality factor of Q = 2.44. Moreover, for sufficiently large Q-factors (Q ≥ 9.75), a second momentum bandgap opens inside the light cone, that is, for propagating waves. The size of the second bandgap grows with the quality factor of the metasurface because resonances with longer lifetimes suffer from smaller radiation losses and require weaker modulation to maintain the same amplification rate. When the quality factor takes sufficiently large values, the two bandgaps merge and the metasurface can amplify incident waves with all possible momenta k ∣ ∣ (see Fig. 3f).
We place a dipole emitter above the metasurface to demonstrate this infinite momentum bandgap (see Fig. 3g). The dipole radiation includes a wide spectrum of momenta, as shown in the upper panel of the figure. Once the temporal modulation of the metasurface is on, waves with all different momenta are amplified and radiated in the specular and retro-directions with respect to the source; see the lower panel in Fig. 3g. This leads to interesting possibilities such as amplified emission and lasing of light from a radiation source6. In contrast to the idea suggested in ref. 6, due to the substantially enhanced bandgap, it is possible here to amplify emission with a large and, in principle, tunable spectrum of wavenumbers. This provides opportunities for beam shaping of the amplified signal and for creating perfect lenses31. Indeed, the evanescent wave content of the source radiation can be reconstructed effectively thanks to the amplification of the wide range of k ∣ ∣. In Supplementary Section 5, we demonstrate that evanescent and propagating wave components of the radiating dipole are amplified by the metasurface in reflection and transmission regimes.
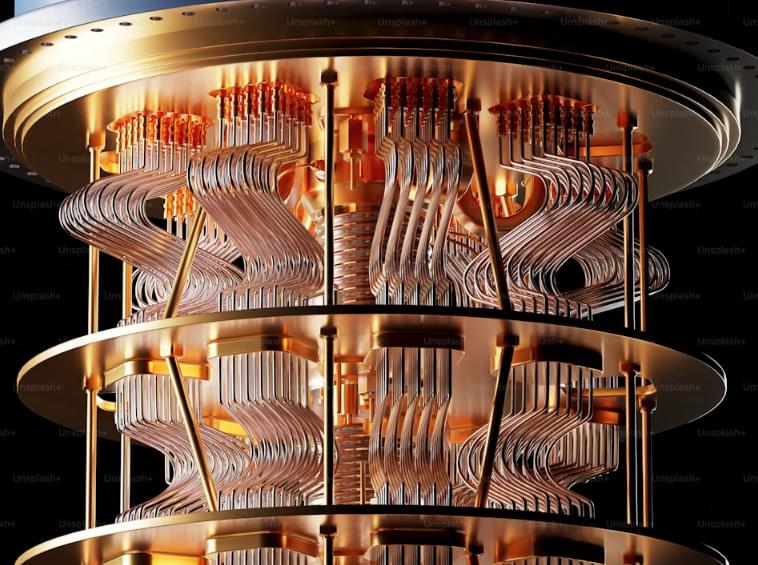
To provide a feasible optical realization of the resonant PTC, we consider a penetrable metasurface surrounded by air and consisting of dielectric nanospheres that are made of a material with a time-varying permittivity (see Fig. 4a). Each nanosphere effectively behaves as an LC resonator as it supports Mie resonances32. For simplicity, we initially ignore material dispersion. The permittivity associated with each nanosphere reads \(\varepsilon (t)=1+{\chi }_{0}[1+m\cos ({\omega }_{{\rm{m}}}t)]\). Varying the permittivity in time modulates the Mie resonance frequencies of the nanospheres (see Fig. 2b). In the following, we rely on the T-matrix method to study the optical response from such a metasurface33 (see Methods and Supplementary Section 6 for details).