Page 11311
Mar 1, 2016
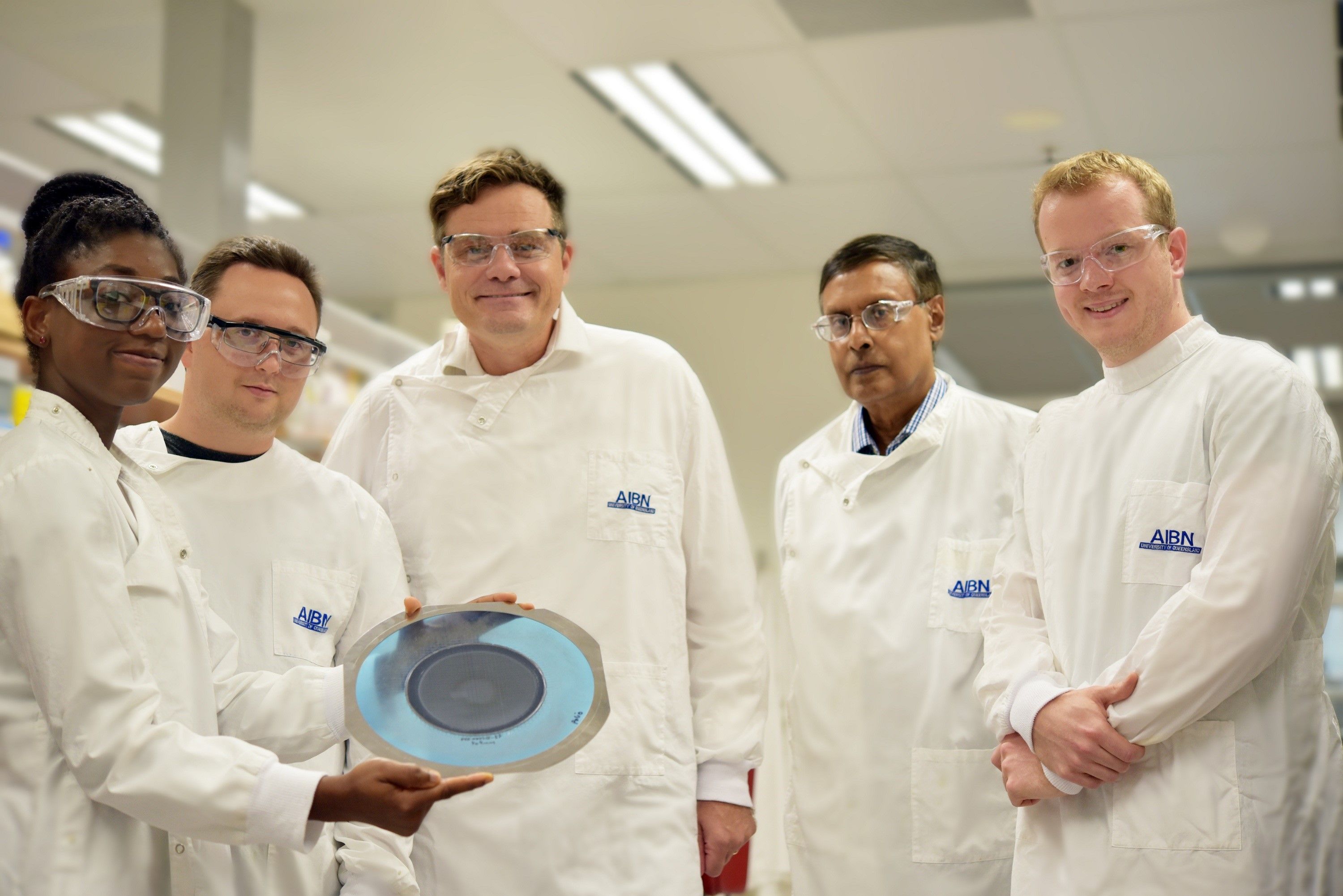
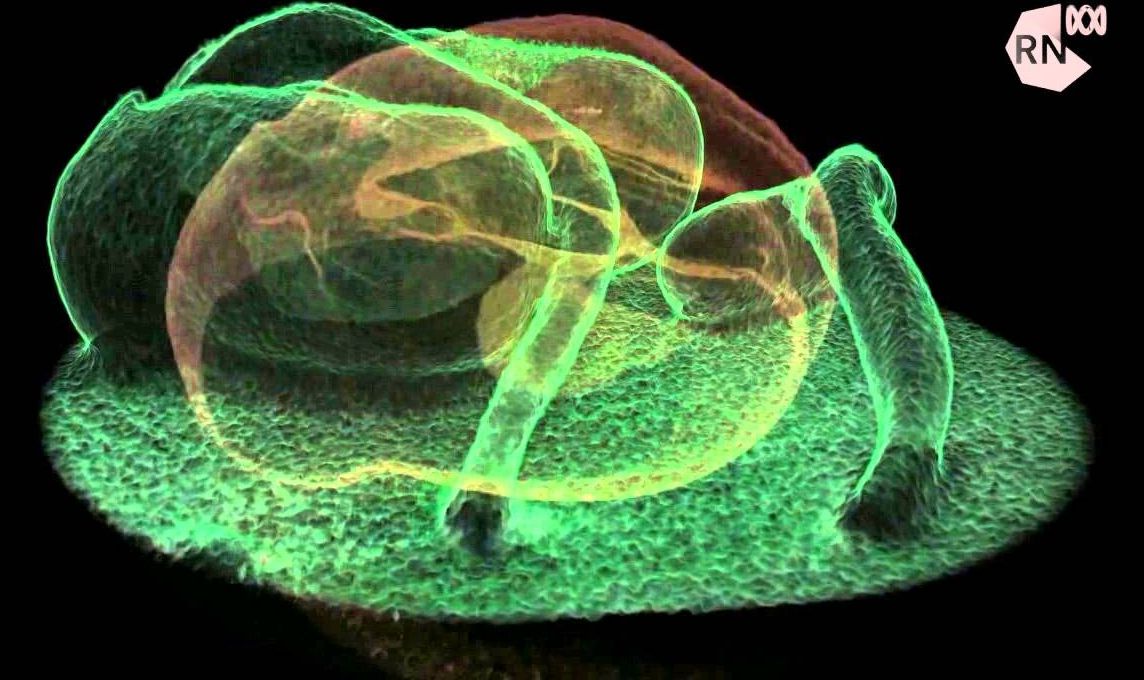
Nanopatch polio vaccine success
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, health, nanotechnology
Needle-free Nanopatch technology developed at The University of Queensland has been used to successfully deliver an inactivated poliovirus vaccine.
Delivery of a polio vaccine with the Nanopatch was demonstrated by UQ’s Professor Mark Kendall and his research team at UQ’s Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, in collaboration with the World Health Organisation, the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, and vaccine technology company Vaxxas.
Professor Kendall said the Nanopatch had been used to administer an inactivated Type 2 poliovirus vaccine in a rat model.
Mar 1, 2016
Triple entanglement paves way for quantum encryption
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: encryption, quantum physics
Mar 1, 2016
There Will Be Netflix on Mars
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, internet, space
Mar 1, 2016
In the Future You’ll Be a Superhero and Here’s How You’ll Get Your Superpowers
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: engineering, futurism
The knock on superheroes is that they’re unrealistic. This isn’t fair. Many superheroes have powers that we are close to or will be capable of engineering for ourselves. What’s unrealistic is the way those powers are doled out. Radioactive spiders aren’t going to make anyone strong any time soon.
Throw away those old origin stories and replace them with new scientific narratives and you’ve got something closer to the truth, which is this: We’re all going to have superpowers. Here’s the order in which we’re going to get them.
Superhuman Marksmanship
Continue reading “In the Future You’ll Be a Superhero and Here’s How You’ll Get Your Superpowers” »
Mar 1, 2016
What was Ray Kurzweil saying about the future in 1990?
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: internet, Ray Kurzweil
Mar 1, 2016
Utilities Cautioned About Potential for a Cyberattack After Ukraine’s
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: cybercrime/malcode, energy
Working remotely, attackers conducted “extensive reconnaissance” of the Ukraine power system’s networks, stole the credentials of operators and learned how to switch off the breakers, plunging more than 225,000 Ukrainians into darkness.
Mar 1, 2016
Scott Aaronson On The Relevance Of Quantum Mechanics To Brain Preservation, Uploading, And Identity
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, mathematics, neuroscience, quantum physics
Biography : Scott Aaronson is an Associate Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT. His research interests center around the capabilities and limits of quantum computers, and computational complexity theory more generally. He also has written about consciousness and personal identity and the relevance of quantum mechanics to these issues.
Michael Cerullo: Thanks for taking the time to talk with me. Given the recent advances in brain preservation, questions of personal identity are moving from merely academic to extremely practical questions. I want to focus on your ideas related to the relevance of quantum mechanics to consciousness and personal identity which are found in your paper “Ghost in the Quantum Turing Machine” ( http://arxiv.org/abs/1306.0159 ), your blog “Could a Quantum Computer Have Subjective Experience?” ( http://www.scottaaronson.com/blog/?p=1951 ), and your book “Quantum Computing since Democritus” ( http://www.scottaaronson.com/democritus/) .
Before we get to your own speculations in this field I want to review some of the prior work of Roger Penrose and Stuart Hameroff ( http://www.quantumconsciousness.org/content/hameroff-penrose…-or-theory ). Let me try to summarize some of the criticism of their work (including some of your own critiques of their theory). Penrose and Hameroff abandon conventional wisdom in neuroscience (i.e. that neurons are the essential computational element in the brain) and instead posit that the microtubules (which conventional neuroscience tell us are involved in nucleic and cell division, organization of intracellular structure, and intracellular transport, as well as ciliary and flagellar motility) are an essential part of the computational structure of the brain. Specifically, they claim the microtubules are quantum computers that grant a person the ability to perform non-computable computations (and Penrose claims these kinds of computations are necessary for things like mathematical understanding). The main critiques of their theory are: it relies on future results in quantum gravity that don’t exist; there is no empirical evidence that microtubules are relevant to the function of the brain; work in quantum decoherence also makes it extremely unlikely that the brain is a quatum computer; even if a brain could somehow compute non-computable functions it isn’t clear what this has to do with consciousness. Would you say these are fair criticisms of their theory and are there any other criticisms you see as relevant?
Mar 1, 2016
Electrifying Drone Race Tests Pilots‘ Sky-High Skills
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in category: drones

https://youtube.com/watch?v=0gYkZGOTdM0
With the first round of the Drone Racing League’s Level 1 race finished, eight pilots will compete for a spot in the finals.
Mar 1, 2016
Inside the Artificial Intelligence Revolution: A Special Report, Pt. 1 — By Jeff Goodall | Rolling Stone
Posted by Odette Bohr Dienel in category: robotics/AI
“For better or worse, whatever future we create, it will be the one we design and build for ourselves. To paraphrase an old adage about the structure of the universe: It’s humans all the way down.”