Sep 6, 2024
Graphene-based wearable strain sensor can detect and broadcast silently mouthed words
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: computing, wearables
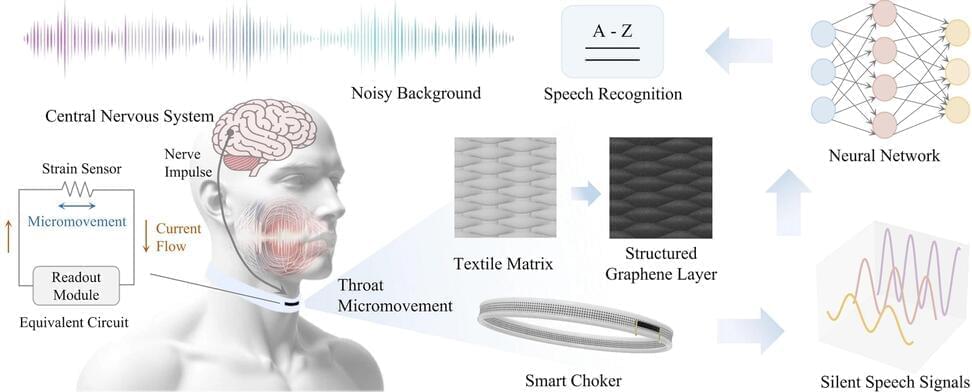
A wearable ‘smart’ choker for speech recognition has the potential to redefine the field of silent speech interface (SSI), say researchers—thanks to embedded ultrasensitive textile strain sensor technology.
Where verbal communication is hindered, such as in locations with lots of background noise or where an individual has an existing speech impairment, SSI systems are a cutting-edge solution, enabling verbal communication without vocalization. As such, it is a type of electronic lip-reading using human-computer interaction.
In new research, led by the University of Cambridge, an overlying structured graphene layer is applied to an integrated textile strain sensor for robust speech recognition performance, even in noisy environments.