(Tech Xplore)—A team of researchers at the University of Wisconsin has developed a pair of glasses that allows the wearer to have tetrachromatic vision. In their paper uploaded to the arXiv preprint sever, the group describes the inspiration for their glasses and explain how they work.
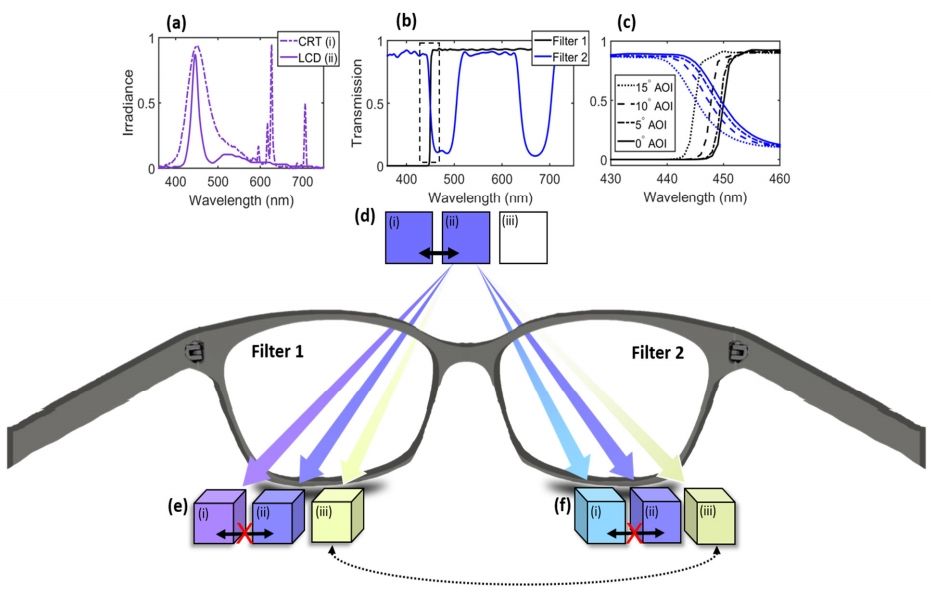
Humans have three types of cone cells in the back of the eye to differentiate color. Some react to blue, some to green and some to red. The cones do their work by responding to the difference in wavelength of the incoming light. Such vision is known as trichromatic. In this new effort, the researchers have found a way of fooling the brain into seeing as if there were a fourth type of cone, by wearing glasses with two types of filters. The result is tetrachromatic vision.
To create the glasses, the researchers fashioned two types of filters, one for each eye. The filters remove some parts of the blue light spectrum. But the filters each remove a different part. When the filters are fitted into a frame and worn like regular glasses, the wearer is able to see colors that are normally hidden—metamers. In a sense, it is rather the opposite of what occurs with people who are color blind. They might see blue and red as the same, even though there is more light information there. Adding spectrum identification to color blind eyes allows for seeing more of what is already there. With the new combined filter system, a person is able to look at what appears to be an object that is all the same color, such as purple, and see more colors in it—those normally hidden metamers.
Continue reading “Double filters allow for tetrachromatic vision in humans” »