Page 10354
Dec 22, 2016
The sound of quantum vacuum
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: media & arts, quantum physics
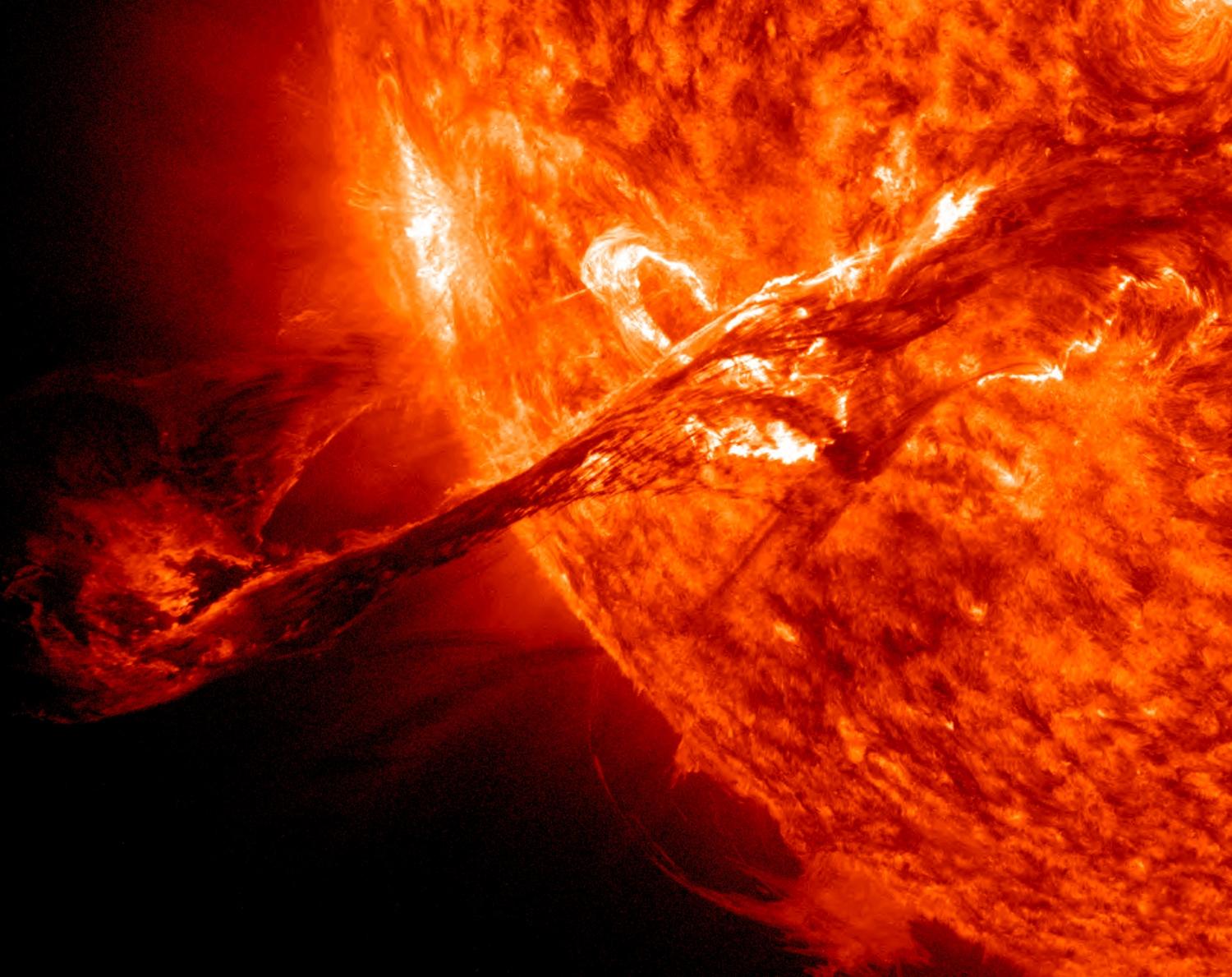
Quantum mechanics dictates sensitivity limits in the measurements of displacement, velocity and acceleration. A recent experiment at the Niels Bohr Institute probes these limits, analyzing how quantum fluctuations set a sensor membrane into motion in the process of a measurement. The membrane is an accurate model for future ultraprecise quantum sensors, whose complex nature may even hold the key to overcome fundamental quantum limits. The results are published in the scientific journal, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Vibrating strings and membranes are at the heart of many musical instruments. Plucking a string excites it to vibrations, at a frequency determined by its length and tension. Apart from the fundamental frequency — corresponding to the musical note — the string also vibrates at higher frequencies. These overtones influence how we perceive the ‘sound’ of the instrument, and allow us to tell a guitar from a violin. Similarly, beating a drumhead excites vibrations at a number of frequencies simultaneously.
These matters are not different when scaling down, from the half-meter bass drum in a classic orchestra to the half-millimeter-sized membrane studied recently at the Niels Bohr Institute. And yet, some things are not the same at all: using sophisticated optical measurement techniques, a team lead by Professor Albert Schliesser could show that the membrane’s vibrations, including all its overtones, follow the strange laws of quantum mechanics. In their experiment, these quantum laws implied that the mere attempt to precisely measure the membrane vibrations sets it into motion. As if looking at a drum already made it hum!
Dec 22, 2016
How These Australian Scientists Proved Time Travel Is Possible
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: entertainment, quantum physics, time travel
Time travel is one of those concepts most often left for fantasy novels, movies, and long conversations about the what-ifs of life. But for many researchers, it’s been a plausible reality for decades.
Dec 22, 2016
The hidden inferno inside your laser pointer
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: physics, space
If you thought that a kid’s room, a Norwegian Nobel Laureate and a laser pointer had nothing in common, two UA physicists are about to enlighten you.
It’s hard to believe, but after having unraveled many of the laws that make the universe tick, physicists still haven’t reached an agreement on whether something as seemingly simple as “hot” or “cold” can be measured in a system under certain circumstances.
“Imagine you threw an iceberg into the sun and right before it’s melted and gone, you wanted to know, ‘How hot is that iceberg at that moment?’ Would that be a meaningful question to ask?” says Charles Stafford, a professor in the Department of Physics in the UA’s College of Science. “According to traditional physics, it wouldn’t be.”
Dec 22, 2016
Sidney Drell, Stanford theoretical physicist and national security expert, dies at 90
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: military, physics, policy, security
RIP dear friend.
A giant in the worlds of both academia and policy, Drell died Wednesday, Dec. 21, at his home in Palo Alto. He was 90 years old.
“An accomplished physicist, his contributions to improve national and international security made our world a better place,” said Tom Gilligan, director of the Hoover Institution at Stanford in a statement. “We are especially grateful for Sid’s relentless dedication to eliminating the threat posed by nuclear weapons and know that his important work will continue to frame the issue.”
Dec 22, 2016
Experts split on how soon quantum computing is coming, but say we should start preparing now
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, encryption, information science, quantum physics
Let’s say closer to 7yrs or less.
Whether quantum computing is 10 years away — or is already here — it promises to make current encryption methods obsolete, so enterprises need to start laying the groundwork for new encryption methods.
A quantum computer uses qubits instead of bits. A bit can be a zero or a one, but a qubit can be both simultaneously, which is weird and hard to program but once folks get it working, it has the potential to be significantly more powerful than any of today’s computers.
Dec 22, 2016
Robots That Read Minds Are a Breakthrough for Manufacturing
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: business, robotics/AI
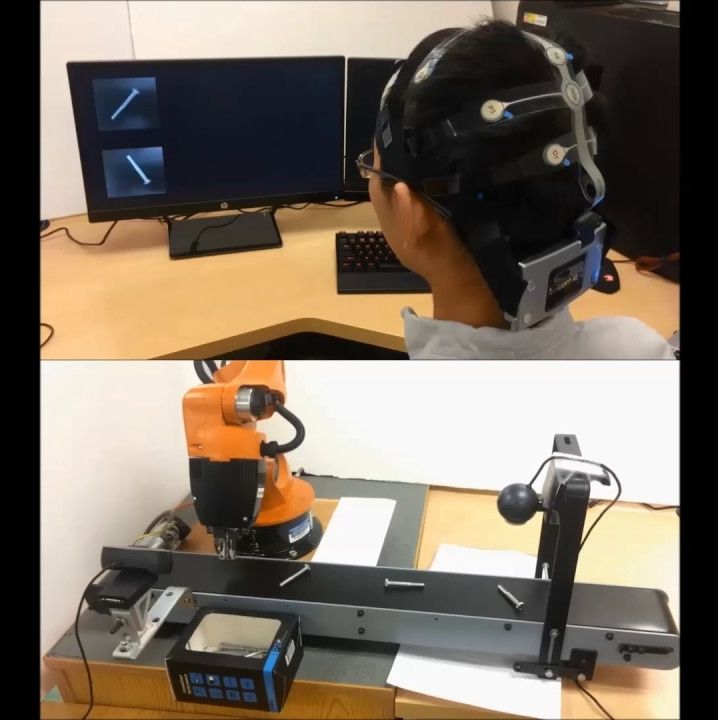

Definitely; why we been telling businesses the importance of BMI for their environments.
A site dedicated to the sciences, recent scientific discoveries and advances.
Continue reading “Robots That Read Minds Are a Breakthrough for Manufacturing” »
Dec 22, 2016
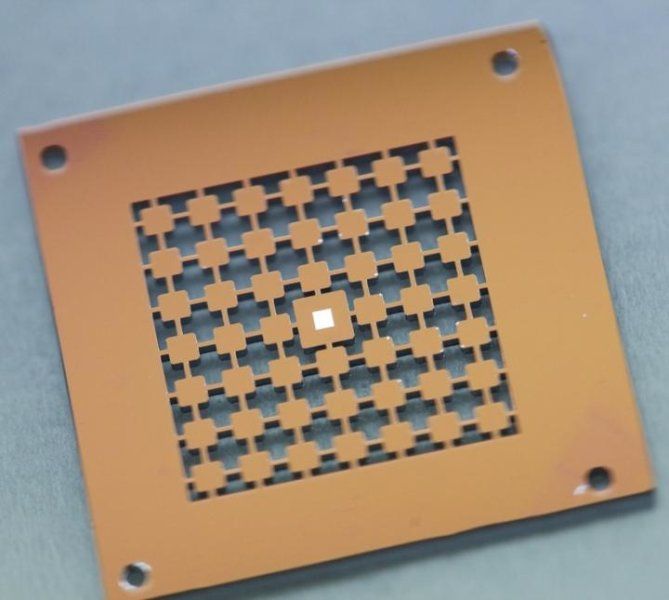
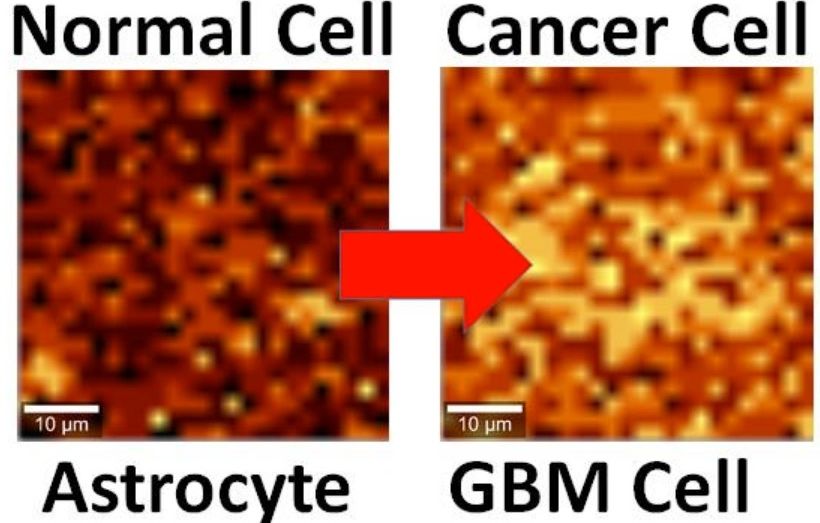
Using graphene to detect brain cancer cells
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Graphene has already proven its importance to brain implants as well as other Synbio technology.
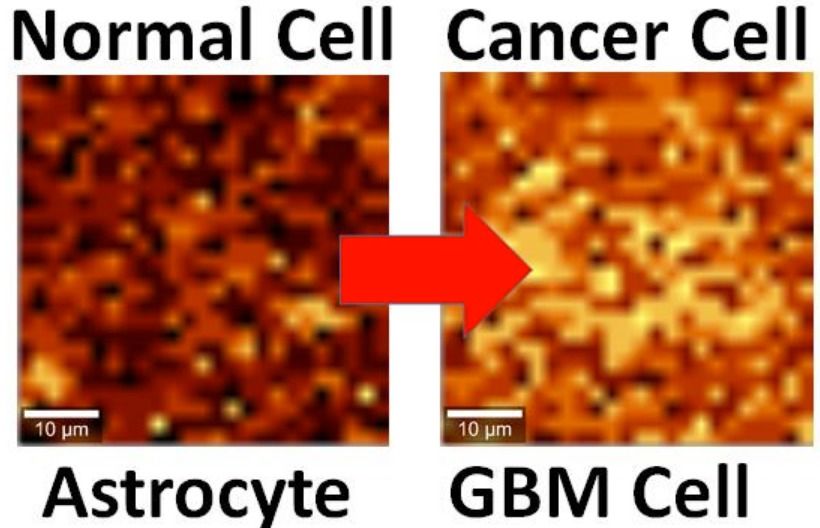
By interfacing brain cells with graphene, University of Illinois at Chicago researchers have differentiated a single hyperactive Glioblastoma Multiforme cancerous astrocyte cell from a normal cell in the lab — pointing the way to developing a simple, noninvasive tool for early cancer diagnosis.
Continue reading “Using graphene to detect brain cancer cells” »
Dec 22, 2016
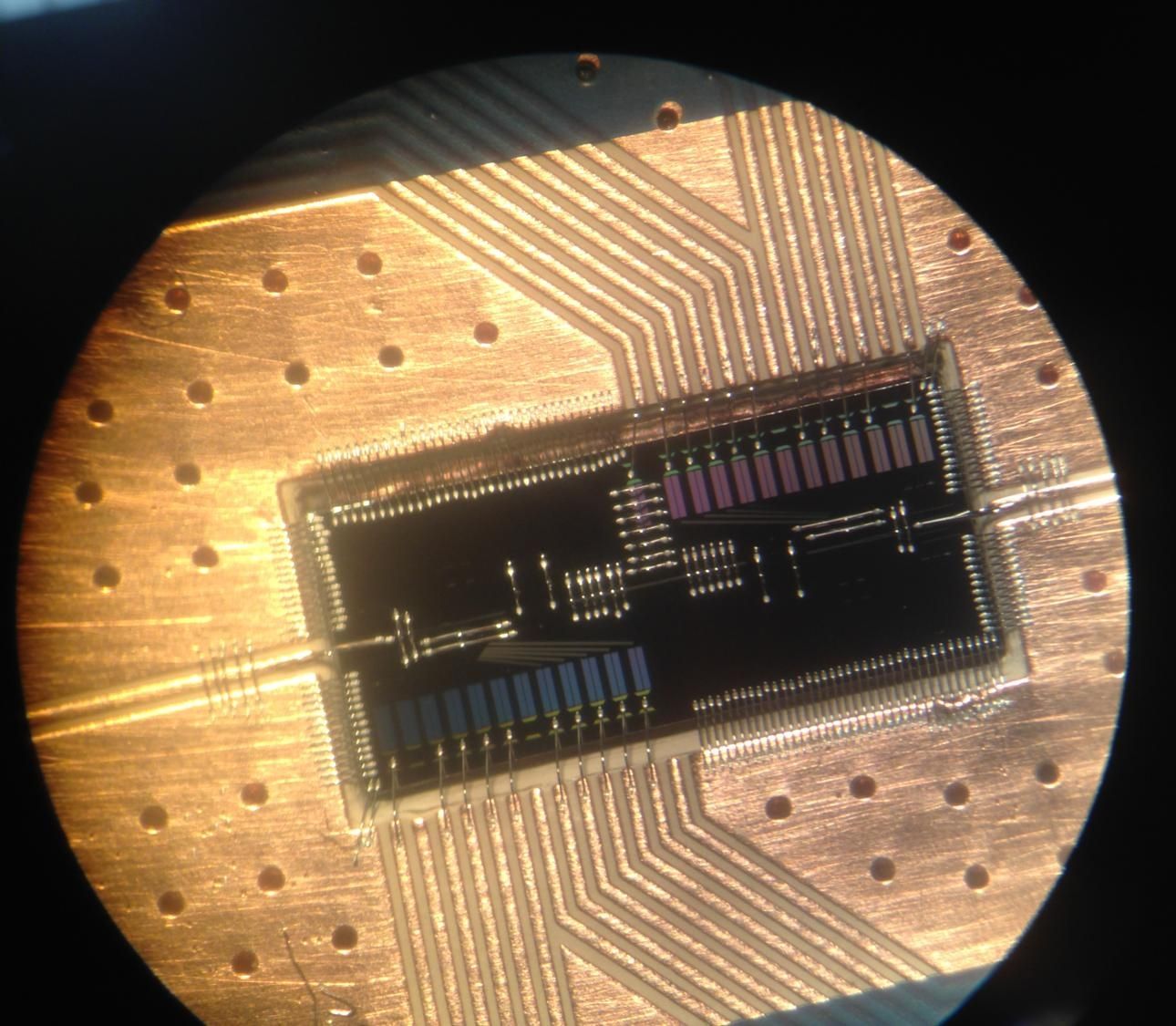
Electron-photon small-talk could have big impact on quantum computing
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, employment, particle physics, quantum physics
In a step that brings silicon-based quantum computers closer to reality, researchers at Princeton University have built a device in which a single electron can pass its quantum information to a particle of light. The particle of light, or photon, can then act as a messenger to carry the information to other electrons, creating connections that form the circuits of a quantum computer.
The research, published in the journal Science and conducted at Princeton and HRL Laboratories in Malibu, California, represents a more than five-year effort to build a robust capability for an electron to talk to a photon, said Jason Petta, a Princeton professor of physics.
“Just like in human interactions, to have good communication a number of things need to work out—it helps to speak the same language and so forth,” Petta said. “We are able to bring the energy of the electronic state into resonance with the light particle, so that the two can talk to each other.”
Continue reading “Electron-photon small-talk could have big impact on quantum computing” »
Dec 22, 2016
The First Quantum Revolution: Foundational information for the enterprise CTO
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: cybercrime/malcode, quantum physics
Our report on Naturally Better Security dove deep into ways quantum effects can be leveraged to enhance real world cybersecurity. It was our most popular post in November 2016 and the feedback we received was taken as a signal that we should produce more on what CTOs should know about the quantum world. With this post we are kicking off a series of five pieces that will dive into quantum effects. This first post tackles some foundational background that puts the science into a historical context. The second one will discuss the current revolution in quantum computing. The third focuses on security concerns. The forth dives into quantum key distribution. The fifth hits on the “so-what” of the current revolution in terms of security.
So first, foundational background on quantum mechanics.
Continue reading “The First Quantum Revolution: Foundational information for the enterprise CTO” »