Page 10272
Feb 26, 2018
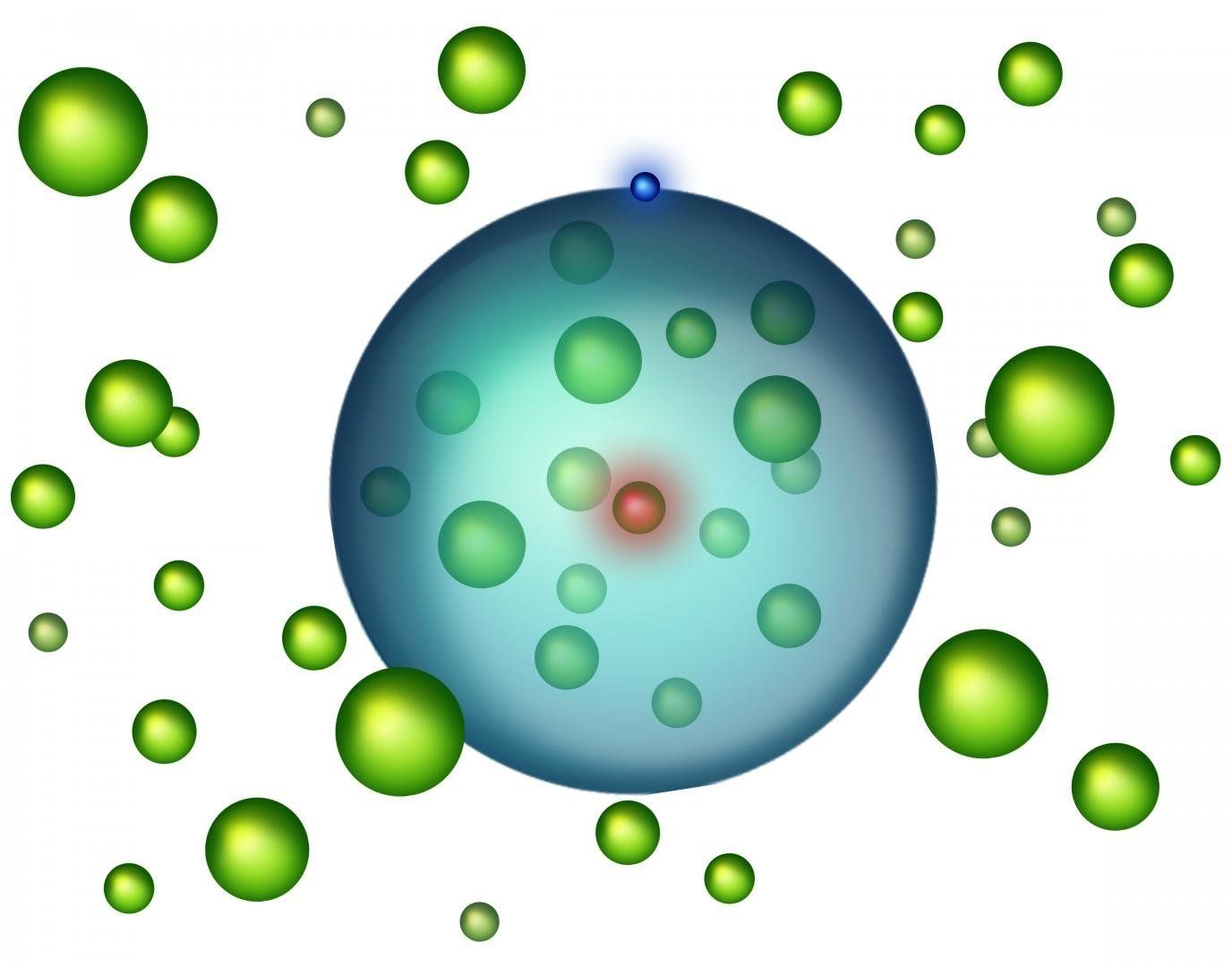
Researchers report the creation of Rydberg polarons in a Bose gas
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: particle physics
What is inside an atom between the nucleus and the electron? Usually there is nothing, but why could there not be other particles too? If the electron orbits the nucleus at a great distance, there is plenty of space in between for other atoms. A “giant atom” could be created, filled with ordinary atoms. All these atoms form a weak bond, creating a new, exotic state of matter at cold temperatures, referred to as Rydberg polarons.
A team of researchers has now presented this state of matter in the journal Physical Review Letters. The theoretical work was done at TU Wien (Vienna) and Harvard University, the experiment was performed at Rice University in Houston (Texas).
Two special fields of atomic physics, which can only be studied in extreme conditions, have been combined in this research project: Bose-Einstein condensates and Rydberg atoms. A Bose-Einstein condensate is a state of matter created by atoms at ultracold temperatures, close to absolute zero. Rydberg atoms are those in which one single electron is lifted into a highly excited state and orbits the nucleus at a very large distance.
Feb 26, 2018
SpaceX’s biggest rival has a ‘genius’ plan to cut its rocket launch costs more than 70%
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: space travel
United Launch Alliance’s upcoming Vulcan rocket will parachute its giant engines back to Earth for reuse, lowering launch costs to $100 million per mission.
Feb 26, 2018
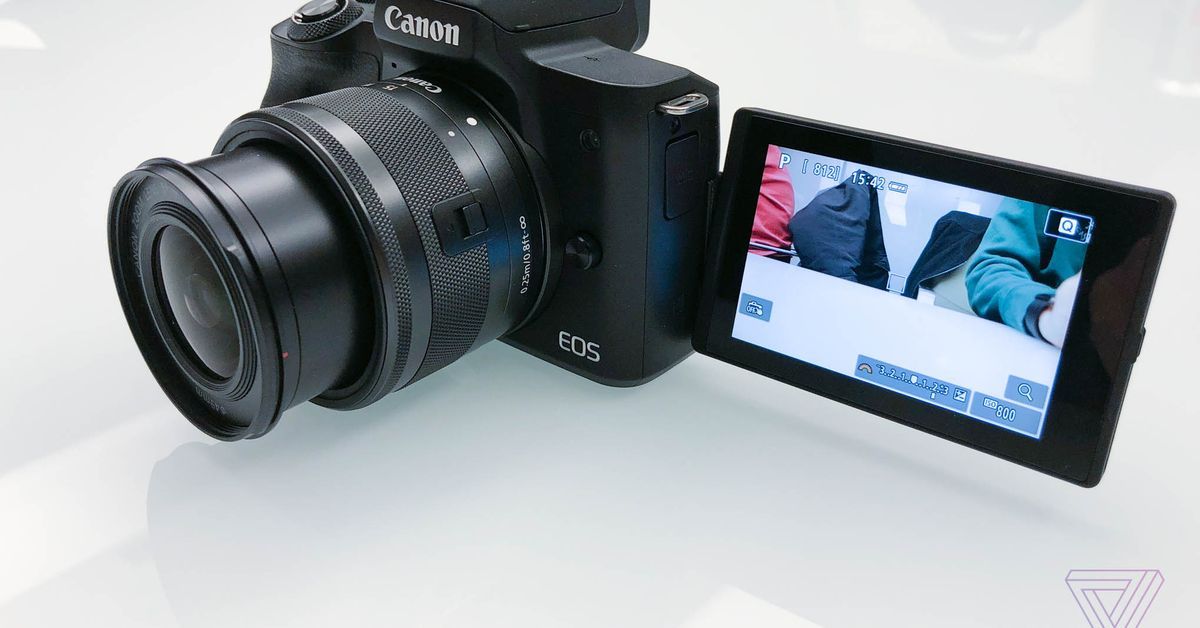
Canon’s newest mirrorless camera shoots 4K video
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: electronics
The new $779 M50 is similar to the M5, but it’s got a new image processor, new RAW file format, a swivel screen, and more.
Feb 26, 2018
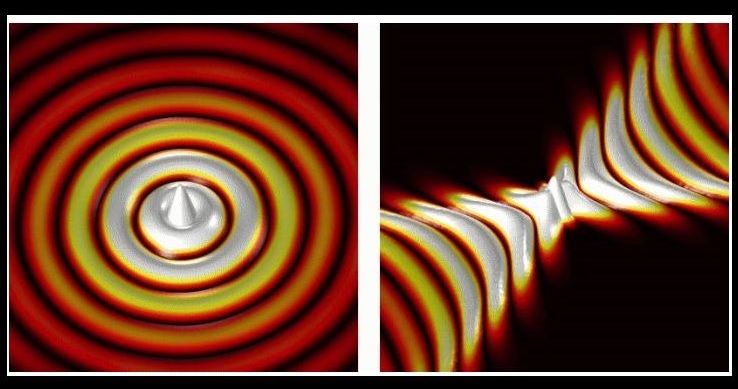
Scientists successfully inverted the circularly propagating optical waves
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: materials
A new study has revealed that the optical waves or light waves can be turned upside down when they are allowed to propagate through specifically structured surfaces. Normally what happens is that the optical waves emerging out from a point source propagate circularly. That means the optical waves traveling away from a point source characteristically display circular, or convex, wavefronts.
The scientists compared these circular wavefronts to the waves seen on the water surface when a stone is dropped into the water. But the latest study revealed that these circularly propagating light waves’ wavefronts can be turned upside down with the help of a special surface. They developed a new material having a hyperbolic metasurface and successfully inverted the optical waves.
The study was led by Peining Li, an EU Marie Sklodowska-Curie fellow at nanoGUNE. According to him, the reason behind this circular propagation of optical waves is because of the fact that the medium through which light waves propagate is isotropic and homogenous. If the waves are isotropic in nature then their propagation is uniform in all direction and being homogenous means they carry the same characteristics throughout the propagation. But these optical waves can be inverted using specifically structured surfaces like the hyperbolic metasurfaces.
Continue reading “Scientists successfully inverted the circularly propagating optical waves” »
Feb 26, 2018
Deep learning for biology
Posted by Derick Lee in categories: biotech/medical, information science, mobile phones, robotics/AI
Finkbeiner’s success highlights how deep learning, one of the most promising branches of artificial intelligence (AI), is making inroads in biology. The algorithms are already infiltrating modern life in smartphones, smart speakers and self-driving cars. In biology, deep-learning algorithms dive into data in ways that humans can’t, detecting features that might otherwise be impossible to catch. Researchers are using the algorithms to classify cellular images, make genomic connections, advance drug discovery and even find links across different data types, from genomics and imaging to electronic medical records.
A popular artificial-intelligence method provides a powerful tool for surveying and classifying biological data. But for the uninitiated, the technology poses significant difficulties.
Feb 25, 2018
Researchers combine metalens with an artificial muscle
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: cyborgs, innovation
Inspired by the human eye, researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have developed an adaptive metalens, that is essentially a flat, electronically controlled artificial eye. The adaptive metalens simultaneously controls for three of the major contributors to blurry images: focus, astigmatism, and image shift.
The research is published in Science Advances.
“This research combines breakthroughs in artificial muscle technology with metalens technology to create a tunable metalens that can change its focus in real time, just like the human eye,” said Alan She, a graduate student at SEAS and first author of the paper. “We go one step further to build the capability of dynamically correcting for aberrations such as astigmatism and image shift, which the human eye cannot naturally do.”
Continue reading “Researchers combine metalens with an artificial muscle” »
Feb 25, 2018
Could Elon Musk Lose the Satellite Market — and Win the Solar System?
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: Elon Musk, satellites, security
When SpaceX launched the world’s biggest rocket ship on Feb. 6, that kind of seemed like a big deal — but not everyone is impressed.
Previewing the SpaceX Falcon Heavy launch, The Wall Street Journal seemed perplexed. Yes, the Falcon Heavy is big, admitted the Journal. But as a “heavy-lift booster,” it said, it is a product designed to serve a market that’s suffering “significantly eroded commercial demand” and “uncertain commercial prospects.”
The problem, as the Journal (correctly) pointed out, is that thanks to advances in rocketry, electronics, and materials technology, “both national security and corporate satellites continue to get smaller and lighter” (and cheaper).
Continue reading “Could Elon Musk Lose the Satellite Market -- and Win the Solar System?” »
Feb 25, 2018
New ‘Metasurface’ Technology Can Turn Light Upside-Down
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: nanotechnology
Feb 25, 2018
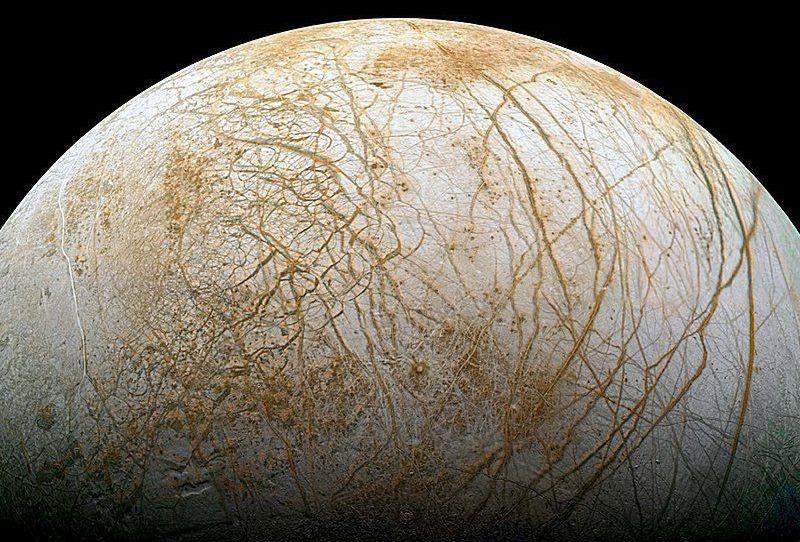
Europa may have hidden liquid ocean to sustain life, new study reveals
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: nuclear energy, space, sustainability
Jupiter is a giant hot gaseous planet situated after the asteroid belt at a distance of 365 million miles when it is the closest w.r.t Earth and 601 million miles when it is the farthest. It was just a few years back when Jupiter’s moon Europa was reported as a potential planet that can hose life. Europa headlined on the internet in 2016 after scientists were able to see water vapor like plumes erupting from its crust. But, as a part of new research at the University of Sao Paulo, Brazil, Europa might have liquid water flowing beneath its 10-kilometer deep ice crust. The researchers used data extracted the data from an analogous location on Earth and found that life is sustainable in even the harsh environment that Europa offers as it has a huge liquid ocean under its crust.
Douglas Galante is the part of the research team that stretched towards the Mponeng Gold Mine in Johannesburg, South Africa in such as evidence. During the research, they found that bacterium Candidatus Desulforudis Audaxviator survives inside the mine at the depth of 2.8 km without any sunlight. It uses the method of water radiolysis where the water molecules are dissociated with the help of ionizing radiation. The analysis of the mine highlighted the cracks that run throughout the mine filled with cracks that supply water containing radioactive uranium which in turns, helps the bacterium to break down water molecules and consume the free radicals produced.
Once the free radicals are generated, these subatomic molecules attack rocks in the surrounding which produces sulfate. This is what these bacteria utilize to synthesize energy and store it without even interacting with the sunlight. One of a kind findings confirmed that it was the very first time when scientists were able to explore a living organism using nuclear energy to survive directly. Galante stated that this ecosystem is analogous to that of Europa’s ocean which has a great amount of thermal energy and absolute zero temperature.
Continue reading “Europa may have hidden liquid ocean to sustain life, new study reveals” »