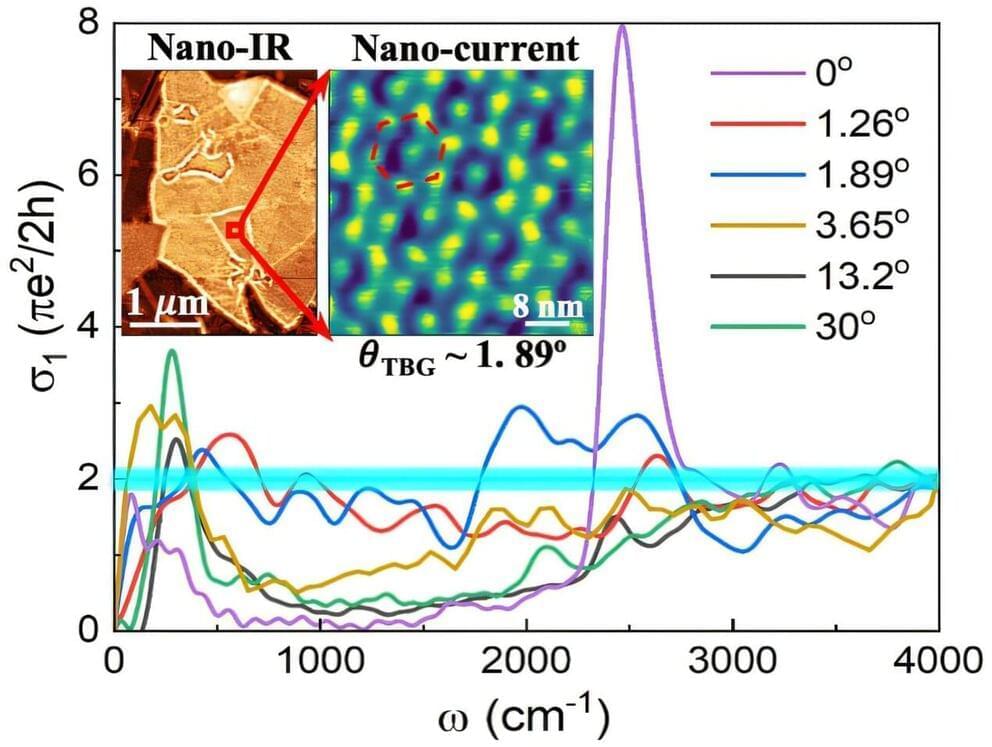
Nov 9, 2024
Innovative transistor for reconfigurable fuzzy logic hardware shows promise for enhanced edge computing
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: computing, innovation
Edge computing devices, devices located in proximity to the source of data instead of in large data centers, could perform computations locally. This could reduce latency, particularly in real-time applications, as it would minimize the need to transfer data from the cloud.