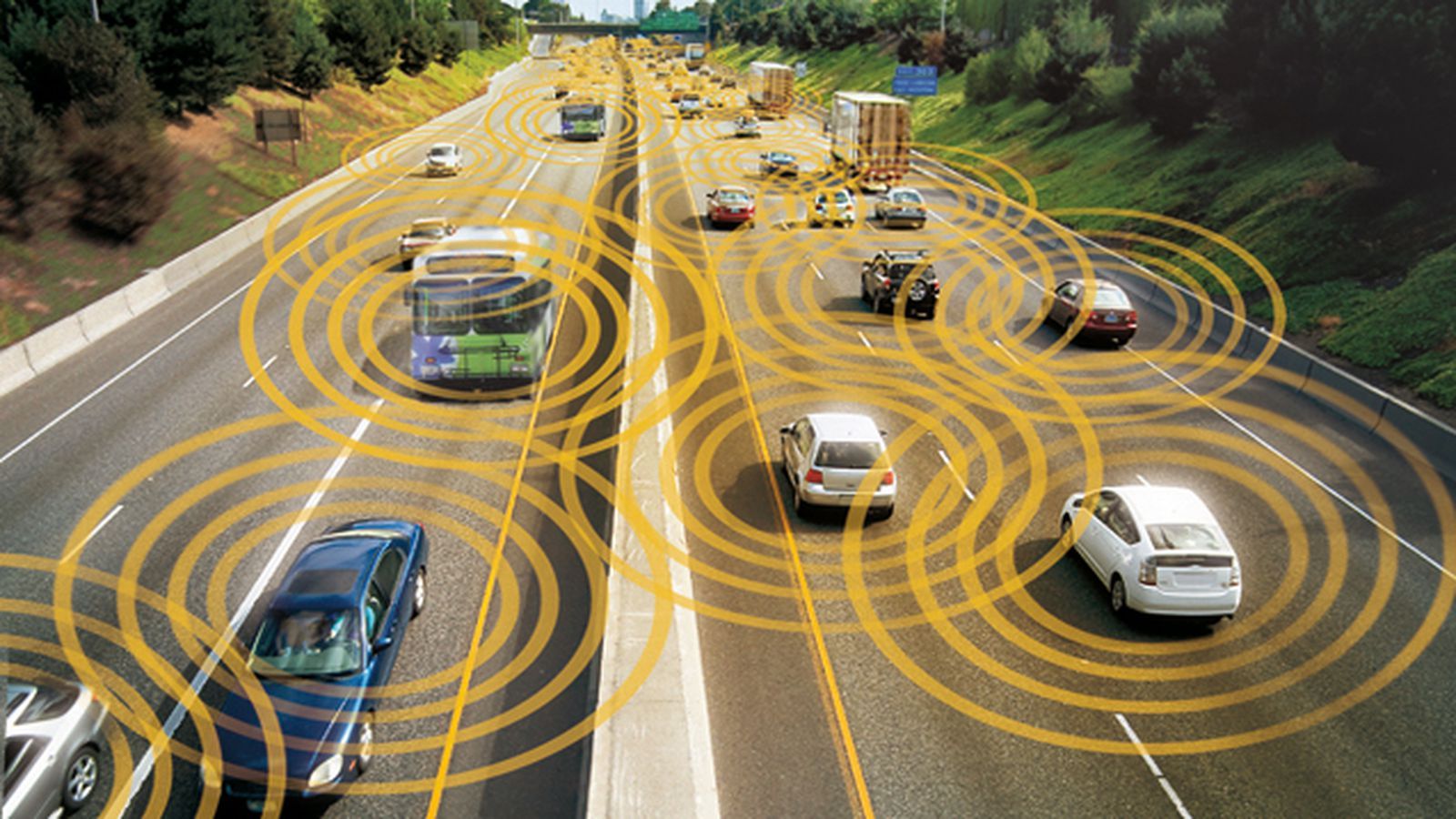
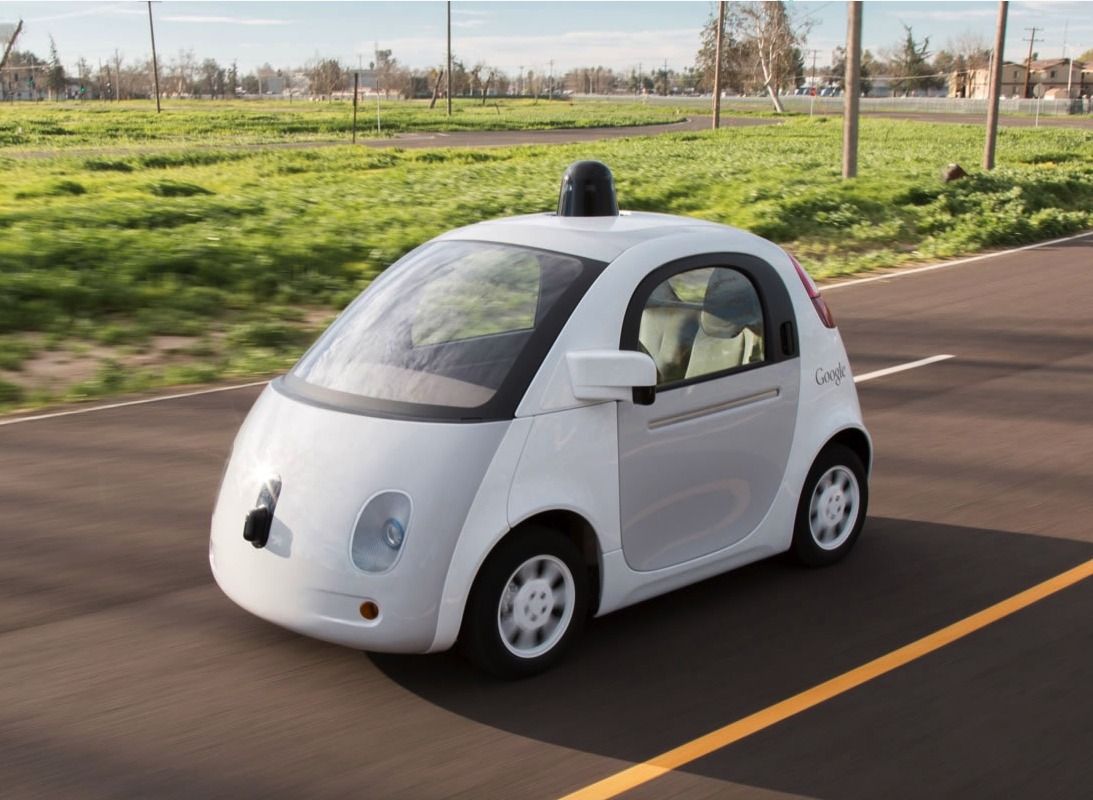
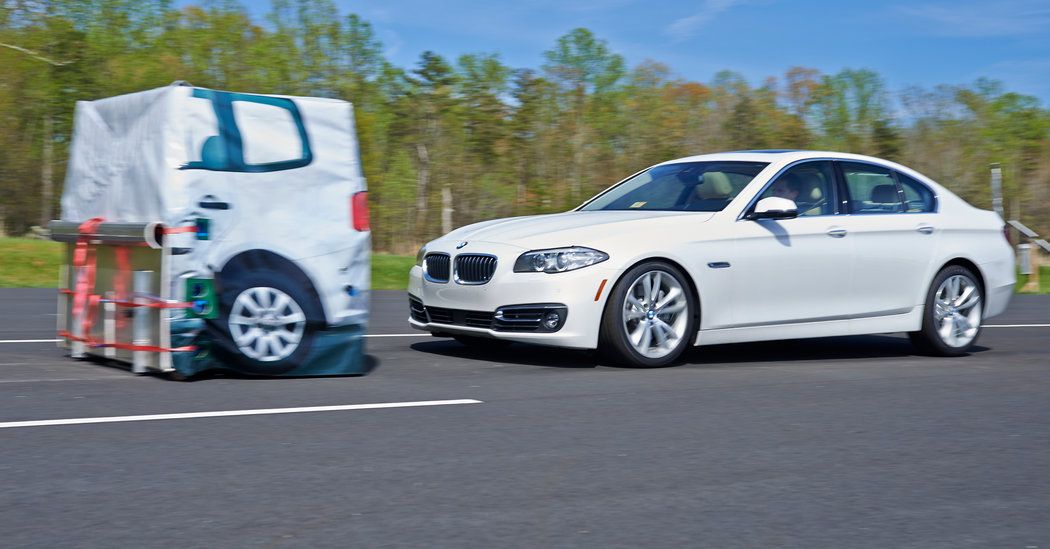
Behind self-driving, vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication is one of the biggest sea changes in transportation technology on the horizon — it could have an enormous impact on driving safety, if it’s implemented quickly and correctly. The concept is pretty simple: cars, signs, and traffic signals all communicate to one another over Wi-Fi-like airwaves, so that drivers (and automatic safety systems built into cars) have more information about the traffic and environment around them. (I got a compelling demo of V2V tech put on by Ford at CES a couple years ago, and I can say that the promise is pretty huge.)
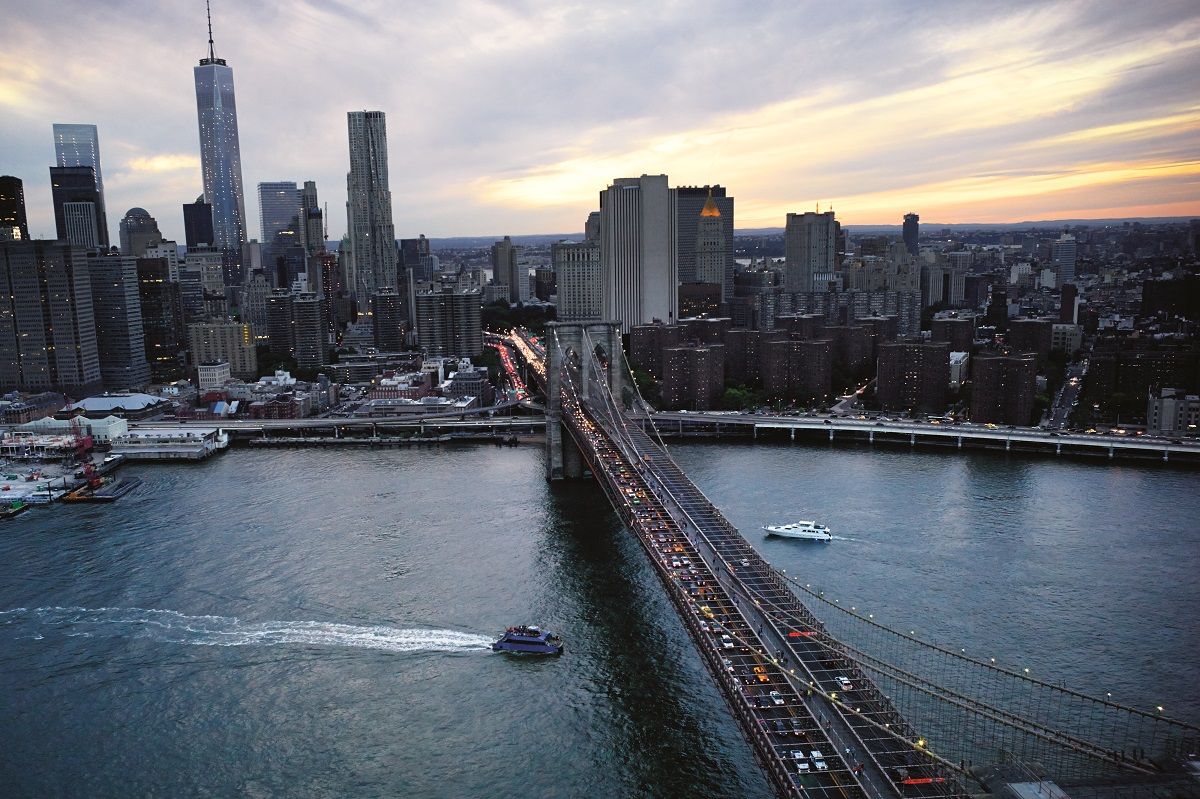
There’s no federal rule in place for requiring V2V yet, but the US Department of Transportation is hoping to get those rules in place by the end of this year — and in the meantime, it’s rolling out huge new pilot programs to put the technology to the test. In the New York City boroughs of Manhattan and Brooklyn, traffic signals will be equipped with V2I hardware, while up to 10,000 city-owned vehicles will be outfitted with V2V. (It’s unclear whether drivers of these vehicles will have access to the data through instrumentation, or whether it’s just being collected as part of the DOT’s ongoing V2V research.)
Read more