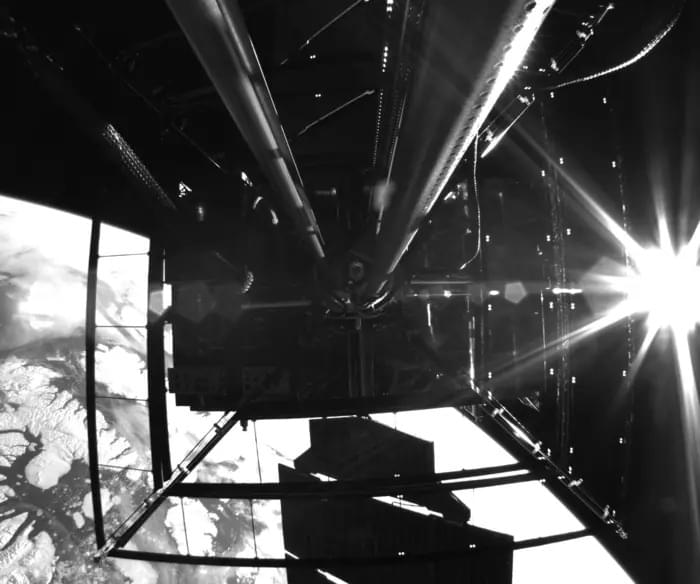
Solar energy is traditionally known for using massive solar panels that collect sunlight and convert it into clean energy, but what if this same energy was instead beamed from satellites in orbit around the Earth, known as space solar power? This is the goal of Space Solar Power Demonstrator (SSPD-1), which is a 110-pound (50-kilogram) project run by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). SSPD-1 was launched onboard the SpaceX Transporter-6 mission on January 3, 2023, and recently concluded its mission after conducting a series of experiments, including the ability to wirelessly beam solar power from space to Earth, which it accomplished in early 2023.
“Solar power beamed from space at commercial rates, lighting the globe, is still a future prospect. But this critical mission demonstrated that it should be an achievable future,” said Dr. Thomas F. Rosenbaum, who is the President of Caltech and the Sonja and William Davidow Presidential Chair and professor of physics.
SSPD-1 successfully demonstrated three experiments during its one-year mission: DOLCE (Deployable on-Orbit ultraLight Composite Experiment), ALBA, and MAPLE (Microwave Array for Power-transfer Low-orbit Experiment). DOLCE demonstrated the architecture necessary for developing space solar power, ALBA demonstrated how to harness solar energy in space, and MAPLE demonstrated how this energy could be wirelessly beamed to Earth.