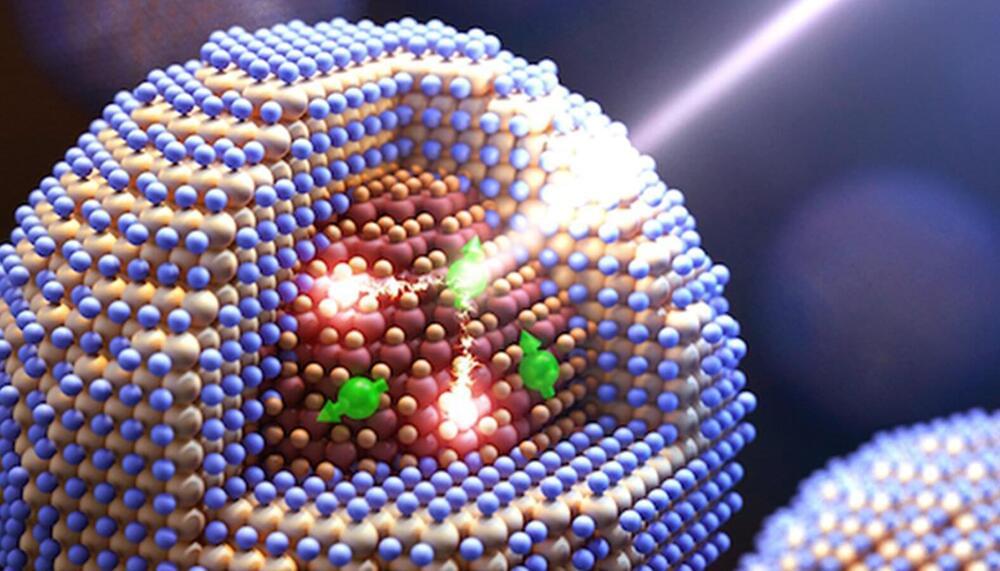
A new approach to developing semiconductor materials at tiny scales could help boost applications that rely on converting light to energy. A Los Alamos-led research team incorporated magnetic dopants into specially engineered colloidal quantum dots—nanoscale-size semiconductor crystals—and was able to achieve effects that may power solar cell technology, photo detectors and applications that depend on light to drive chemical reactions.
“In quantum dots comprising a lead-selenide core and a cadmium-selenide shell, manganese ions act as tiny magnets whose magnetic spins strongly interact with both the core and the shell of the quantum dot,” said Victor Klimov, leader of the Los Alamos nanotechnology team and the project’s principal investigator. “In the course of these interactions, energy can be transferred to and from the manganese ion by flipping its spin—a process commonly termed spin exchange.”
In spin-exchange carrier multiplication, a single absorbed photon generates not one but two electron-hole pairs, also known as excitons, which occur as a result of spin-flip relaxation of an excited manganese ion.