Jul 26, 2016
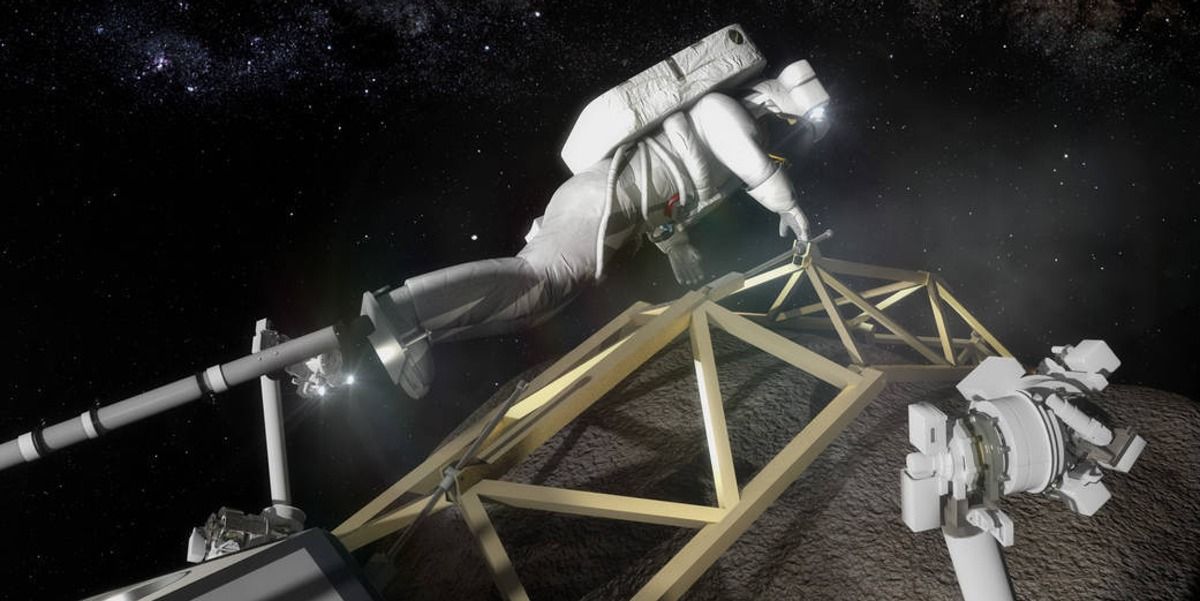
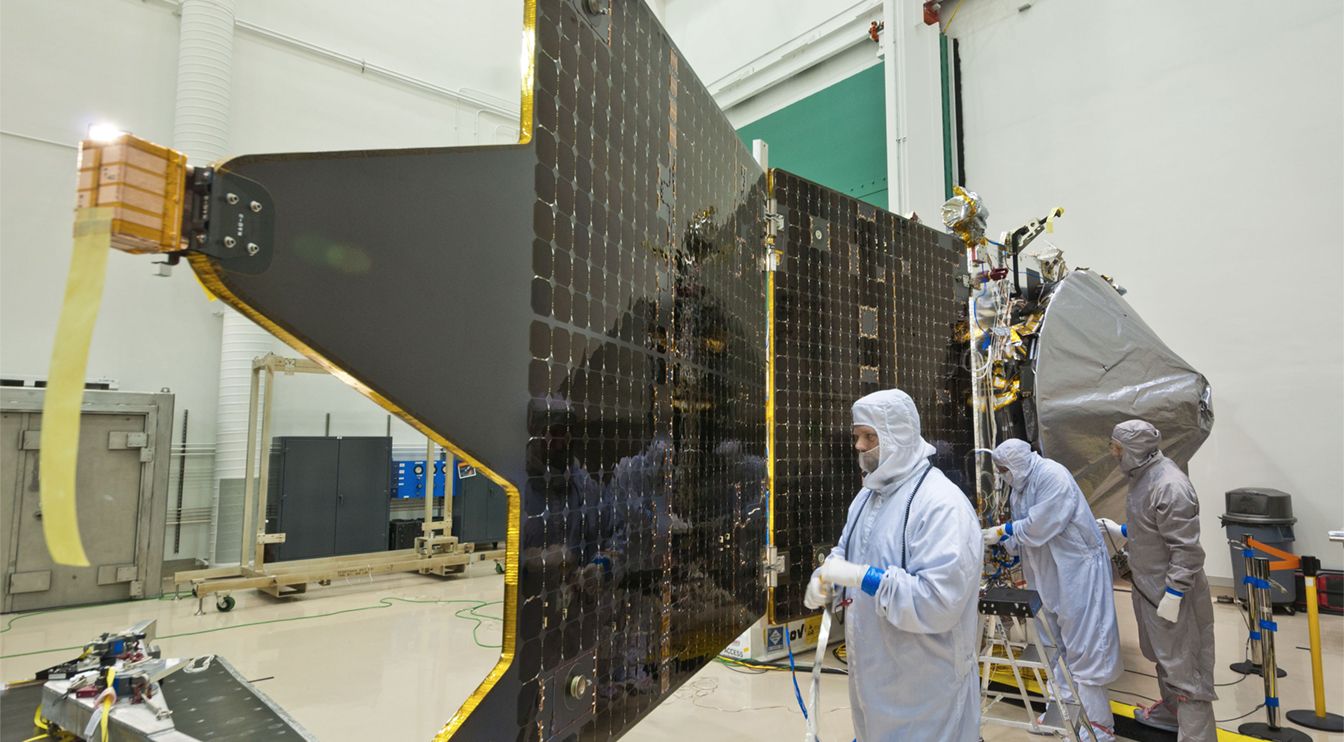
NASA’s Weird Asteroid Redirect Mission Is Actually Making Progress
Posted by Andreas Matt in category: space
Other NASA officials have said they have plans to speak with Congressional staffers about ARM and assuage concerns the agency is wasting valuable time and resources on something impractical.
A successful ARM mission would be the craziest thing NASA has ever done, but would also hit on pretty much every big agency objective. ARM would basically kill a dozen space birds with one space rock.
Photos via Screenshot from NASA webcast., NASA.
Continue reading “NASA’s Weird Asteroid Redirect Mission Is Actually Making Progress” »