Mar 22, 2024
Oregon Is Now Home to the World’s Largest Dark Sky Sanctuary
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: space
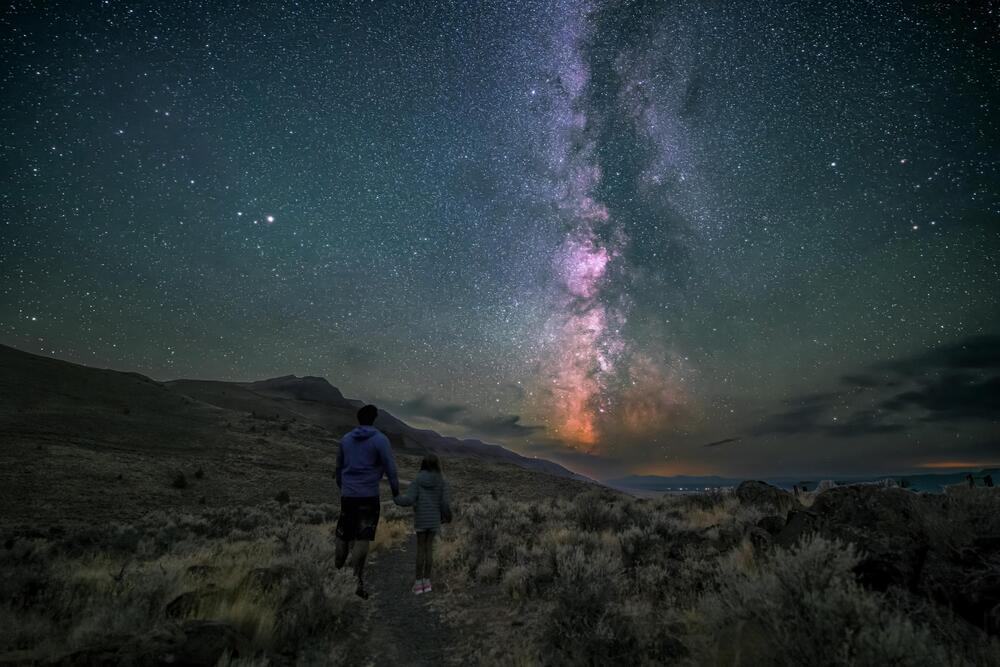
Calling all stargazers: Oregon is now home to the largest Dark Sky Sanctuary in the world.
Earlier this month, DarkSky International certified a remote, 2.5 million-acre area in the southeastern part of the state. From this rugged swath of high desert landscape dotted with sagebrush, visitors who stay up late can see large numbers of stars, planets and other celestial bodies.
“It’s surprising sometimes to see that many stars all at once,” says Bob Hackett, executive director of Travel Southern Oregon, to the Guardian’s Dani Anguiano. “It catches you, and it makes you pause because you feel like you can touch it … That vastness of the whole cosmos up there—it almost makes you get closer to the people you’re with on the ground.”