Sep 6, 2019
AI Aristo takes science test, emerges multiple-choice superstar
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: education, robotics/AI, science
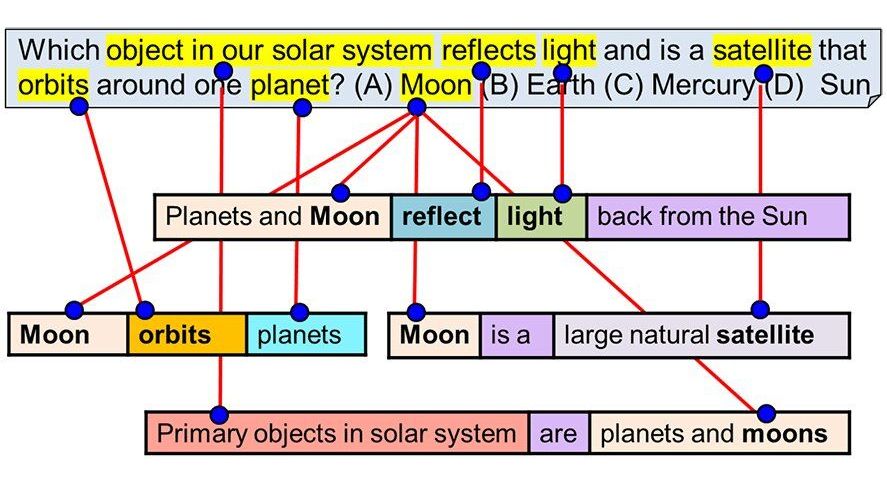
Aristo has passed an American eighth grade science test. If you are told Aristo is an earnest kid who loves to read all he can about Faraday and plays the drums you will say so what, big deal.
Aristo, though, is an artificial intelligence program and scientists would like the world to know this is a big deal, as “a benchmark in AI development,” as Melissa Locker called it in Fast Company.
We mean, just think about it. Cade Metz, in The New York Times, has thought about it. “Four years ago, more than 700 computer scientists competed in a contest to build artificial intelligence that could pass an eighth-grade science test. There was $80,000 in prize money on the line. They all flunked. Even the most sophisticated system couldn’t do better than 60% on the test. AI couldn’t match the language and logic skills that students are expected to have when they enter high school.”