May 23, 2016
China to Launch World’s First Quantum Space Satellite in July
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: government, quantum physics, space
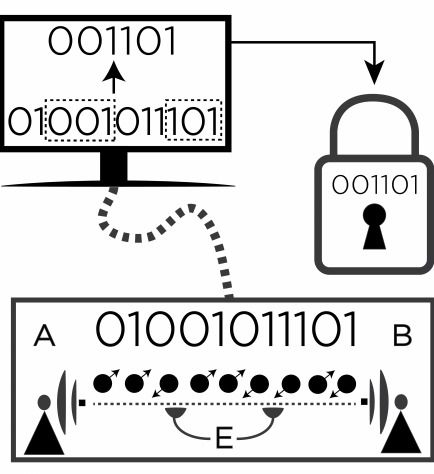
Enough said; China officially makes Quantum communications available via Satellite in July. Now, what does this mean to government funded hackers and the US and Europe?
The launch of the world’s first quantum space satellite developed by China is scheduled for July, according to the project’s chief scientist Pan Jianwei.
BEIJING (Sputnik) — According to the physicist, cited by the People’s Daily Online, the quantum network will connect Beijing, Jinan, Hefei and Shanghai among other cities spanning a 2,000-kilometer (1,243 miles) area.
Continue reading “China to Launch World’s First Quantum Space Satellite in July” »