Oct 18, 2016
Quantum Teleportation Could Revolutionize Modern Phone And Internet Communication
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: encryption, finance, internet, mobile phones, quantum physics, space, transportation
I never get tired of articles highlighting the potential around leveraging Quantum teleporting as a method to replace networks and communications. Now the real question is how soon and how much of the existing infrastructure will need to be replaced to begin taking advantage of this technology earlier than others? As with most things, governments are often early adopters as well as Financial Services and ISPs are a close 2nd in the adoption of such technologies.
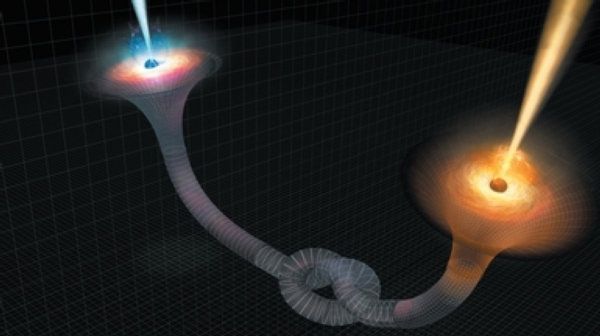
An experiment conducted about quantum teleportation could improve and transform the modern phone and Internet communication by having highly secure and encrypted messaging.
A recent study has suggested that comet outbursts are caused by avalanches and not geysers.