The emergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques is changing the world dramatically with novel applications such as internet of things, autonomous vehicles, real-time imaging processing and big data analytics in healthcare. In 2020, the global data volume is estimated to reach 44 Zettabytes, and it will continue to grow beyond the current capacity of computing and storage devices. At the same time, the related electricity consumption will increase 15 times by 2030, swallowing 8% of the global energy demand. Therefore, reducing energy consumption and increasing speed of information storage technology is in urgent need.
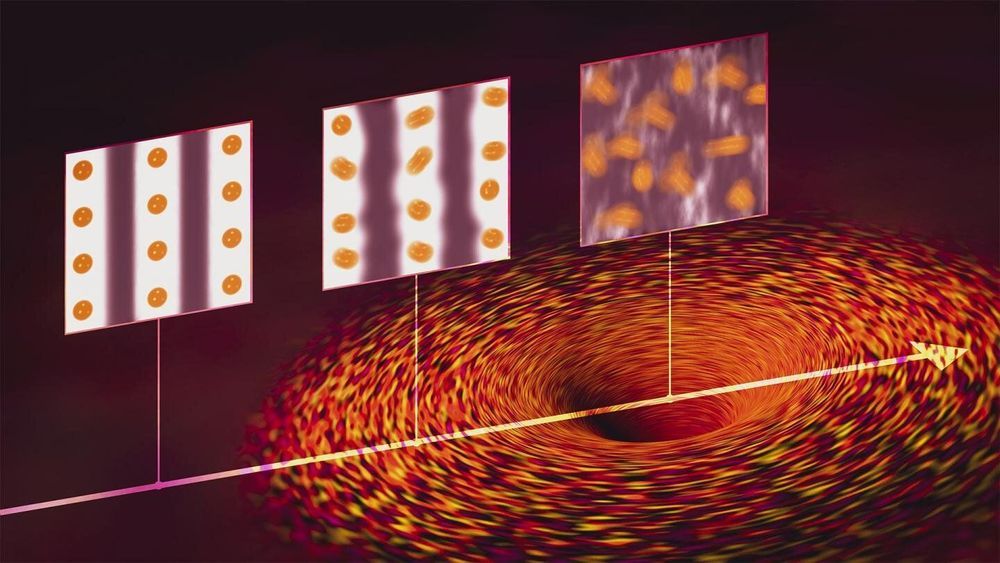
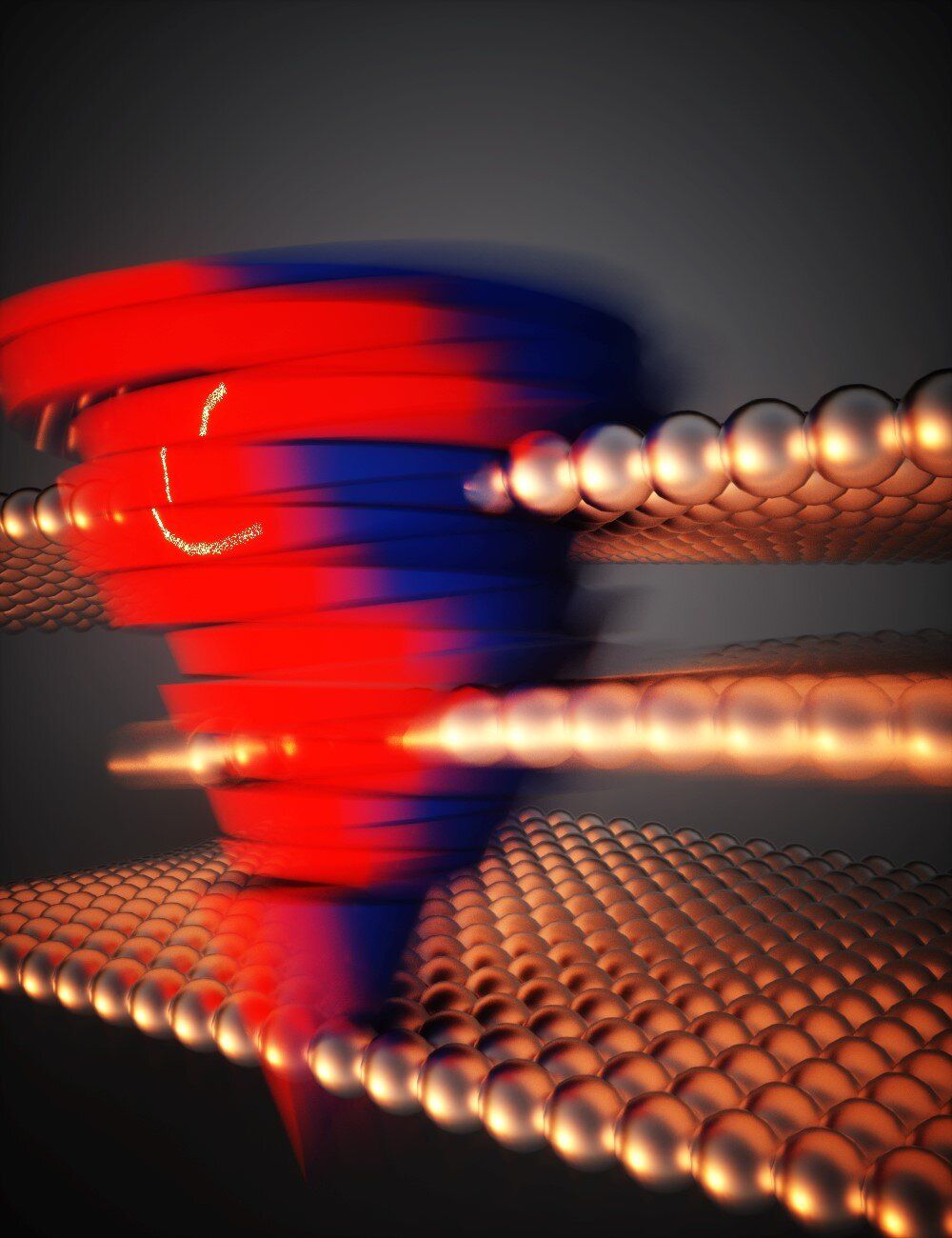
Berkeley researchers led by HKU President Professor Xiang Zhang when he was in Berkeley, in collaboration with Professor Aaron Lindenberg’s team at Stanford University, invented a new data storage method: They make odd numbered layers slide relative to even-number layers in tungsten ditelluride, which is only 3nm thick. The arrangement of these atomic layers represents 0 and 1 for data storage. These researchers creatively make use of quantum geometry: Berry curvature, to read information out. Therefore, this material platform works ideally for memory, with independent ‘write’ and ‘read’ operation. The energy consumption using this novel data storage method can be over 100 times less than the traditional method.
This work is a conceptual innovation for non-volatile storage types and can potentially bring technological revolution. For the first time, the researchers prove that two-dimensional semi-metals, going beyond traditional silicon material, can be used for information storage and reading. This work was published in the latest issue of the journal Nature Physics. Compared with the existing non-volatile (NVW) memory, this new material platform is expected to increase storage speed by two orders and decrease energy cost by three orders, and it can greatly facilitate the realization of emerging in-memory computing and neural network computing.