Nov 14, 2024
Scientists find a new way of entangling light and sound
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: computing, quantum physics
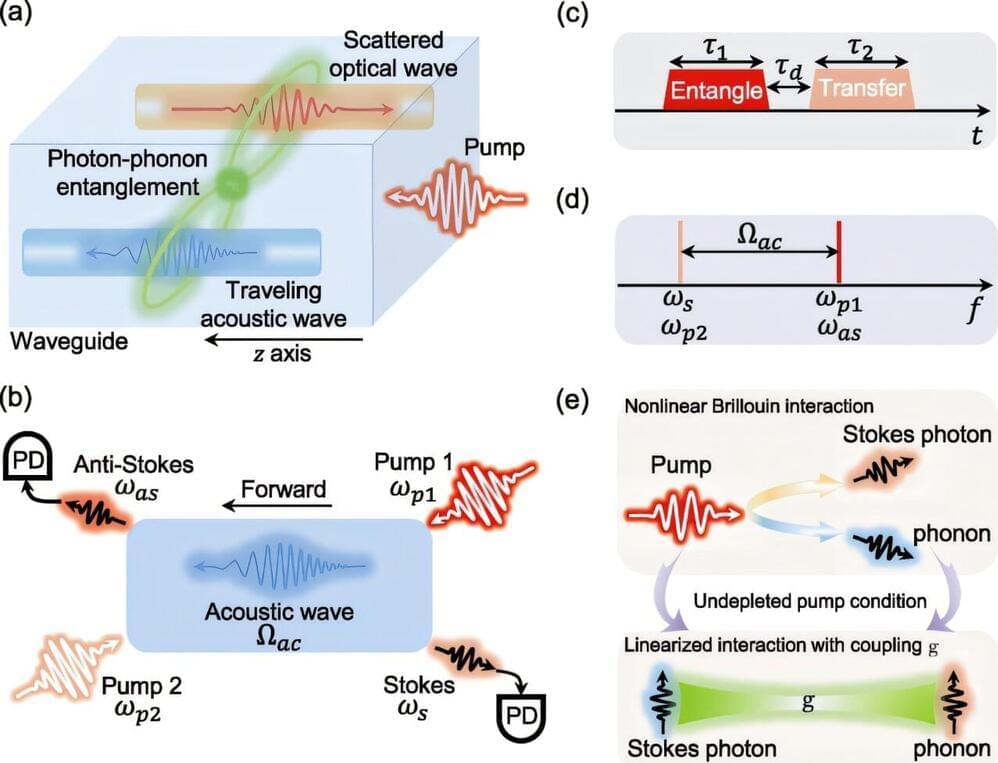
Photons, however, are volatile. Therefore, feasible alternatives are being sought for certain applications, such as quantum memory or quantum repeater schemes. One such alternative is the acoustic domain, where quanta are stored in acoustic or sound waves.
Scientists at the MPL have now indicated a particularly efficient way in which photons can be entangled with acoustic phonons: While the two quanta travel along the same photonic structures, the phonons move at a much slower speed. The underlying effect is the optical nonlinear effect known as Brillouin-Mandelstam scattering. It is responsible for coupling quanta at fundamentally different energy scales.
In their study, the scientists showed that the proposed entangling scheme can operate at temperatures in the tens of Kelvin. This is much higher than those required by standard approaches, which often employ expensive equipment such as dilution fridges. The possibility of implementing this concept in optical fibers or photonic integrated chips makes this mechanism of particular interest for use in modern quantum technologies.