Jun 23, 2023
Cerebellar Excitability Regulates Physical Fatigue Perception
Posted by Dan Kummer in category: neuroscience
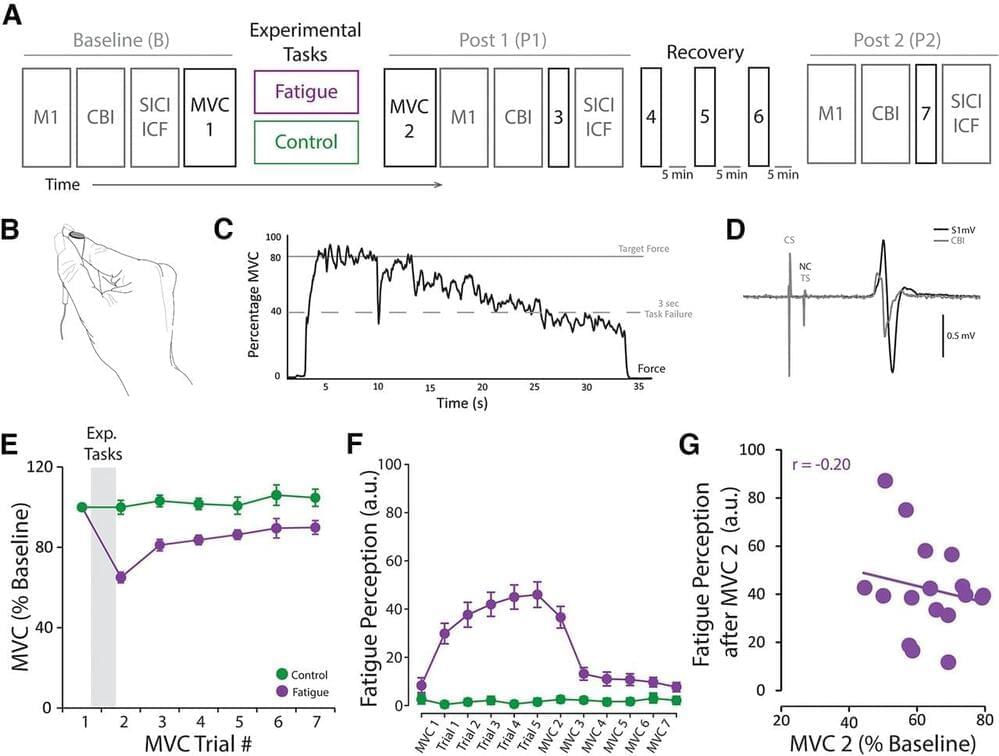
Fatigue is the subjective sensation of weariness, increased sense of effort, or exhaustion and is pervasive in neurologic illnesses. Despite its prevalence, we have a limited understanding of the neurophysiological mechanisms underlying fatigue. The cerebellum, known for its role in motor control and learning, is also involved in perceptual processes. However, the role of the cerebellum in fatigue remains largely unexplored. We performed two experiments to examine whether cerebellar excitability is affected after a fatiguing task and its association with fatigue. Using a crossover design, we assessed cerebellar inhibition (CBI) and perception of fatigue in humans before and after “fatigue” and “control” tasks. Thirty-three participants (16 males, 17 females) performed five isometric pinch trials with their thumb and index finger at 80% maximum voluntary capacity (MVC) until failure (force 40% MVC; fatigue) or at 5% MVC for 30 s (control). We found that reduced CBI after the fatigue task correlated with a milder perception of fatigue. In a follow-up experiment, we investigated the behavioral consequences of reduced CBI after fatigue. We measured CBI, perception of fatigue, and performance during a ballistic goal-directed task before and after the same fatigue and control tasks. We replicated the observation that reduced CBI after the fatigue task correlated with a milder perception of fatigue and found that greater endpoint variability after the fatigue task correlated with reduced CBI. The proportional relation between cerebellar excitability and fatigue indicates a role of the cerebellum in the perception of fatigue, which might come at the expense of motor control.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Fatigue is one of the most common and debilitating symptoms in neurologic, neuropsychiatric, and chronic illnesses. Despite its epidemiological importance, there is a limited understanding of the neurophysiological mechanisms underlying fatigue. In a series of experiments, we demonstrate that decreased cerebellar excitability relates to lesser physical fatigue perception and worse motor control. These results showcase the role of the cerebellum in fatigue regulation and suggest that fatigue-and performance-related processes might compete for cerebellar resources.