Archive for the ‘neuroscience’ category: Page 250
Sep 26, 2023
Elon is Right. Having to Live Forever is a Curse. Here’s How to Solve It
Posted by Montie Adkins in categories: Elon Musk, ethics, life extension, neuroscience

Let’s say that it is a curse. The issue is he is also against life extension entirely. Maybe I want 200 years. Or 1,000. I have zero concern over a boredom problem as it is brain process which can eventually be controlled. And I am disgusted with the idea that I have to die because we might not progress very fast? Ugh.
Elon Musk has said a lot of potentially stupid stuff about aging and longevity, from saying that people shouldn’t live very long because society would ossify to advocating that we judge people based on their chronological age. Most recently, he’s taken to Twitter (aka X) to say “May you live forever is the worst possible curse once you understand deep time.” In this case though, he’s not wrong.
Continue reading “Elon is Right. Having to Live Forever is a Curse. Here’s How to Solve It” »
Sep 26, 2023
Brain implants may get a broadband boost with new approach
Posted by Gemechu Taye in categories: computing, neuroscience, wearables
Researchers have proposed employing wireless neural implants to execute communication between the human brain and computers.
Purdue University researchers have unveiled a new method that may enable a compact brain-implanted sensor to sense and transmit data to a wearable device shaped like headphones.
Sep 26, 2023
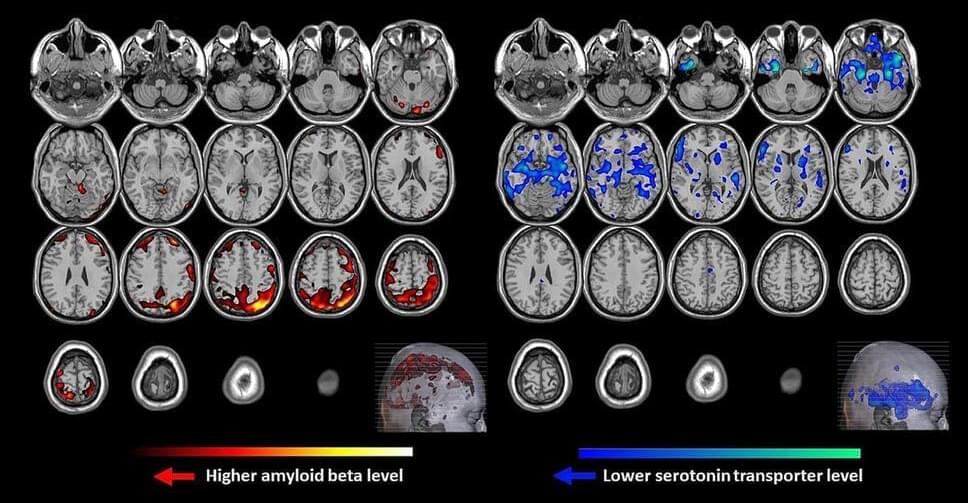
Amyloid Beta and Serotonin May Be Keys to Predicting Who Develops Late-Life Depression
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Image from a Johns Hopkins Medicine study showing PET scans from brains of people with and without late-life depression. The brains of patients with late-life depression show more yellow to red regions (scans on the left), indicating higher amyloid beta protein levels, and more blue regions (scans on the right), indicating lower serotonin transporter levels. Both imaging measures are markers of late-life depression. Credit: Graphic adapted from Smith et al, Nature, Sept. 13, 2021.
Sep 26, 2023
Regeneration across complete spinal cord injuries reverses paralysis
Posted by Dan Kummer in categories: biotech/medical, engineering, neuroscience

When the spinal cords of mice and humans are partially damaged, the initial paralysis is followed by the extensive, spontaneous recovery of motor function. However, after a complete spinal cord injury, this natural repair of the spinal cord doesn’t occur and there is no recovery. Meaningful recovery after severe injuries requires strategies that promote the regeneration of nerve fibers, but the requisite conditions for these strategies to successfully restore motor function have remained elusive.
“Five years ago, we demonstrated that nerve fibers can be regenerated across anatomically complete spinal cord injuries,” says Mark Anderson, a senior author of the study. “But we also realized this wasn’t enough to restore motor function, as the new fibers failed to connect to the right places on the other side of the lesion.” Anderson is the director of Central Nervous System Regeneration at. NeuroRestore and a scientist at the Wyss Center for Bio and Neuroengineering.
Continue reading “Regeneration across complete spinal cord injuries reverses paralysis” »
Sep 25, 2023
Psychedelic drug MDMA eases PTSD symptoms in a study that paves the way for possible US approval
Posted by Brent Ellman in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
The psychedelic drug MDMA can reduce symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder, researchers reported in a new study published Thursday.
The company sponsoring the research said it plans later this year to seek U.S. approval to market the drug, also known as ecstasy, as a PTSD treatment when combined with talk therapy.
“It’s the first innovation in PTSD treatment in more than two decades. And it’s significant because I think it will also open up other innovation,” said Amy Emerson, CEO of MAPS Public Benefit Corporation, the research sponsor.”
Sep 25, 2023
Scientists Just Found a Way to Help Your Brain Work Like It’s 30 Years Younger
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: life extension, neuroscience
Just about everyone may want to look and feel younger and healthier, but multimillion-dollar investments and broccoli smoothies are not for everyone. Still, that doesn’t mean the less hardcore among us are out of luck if we’re hoping to turn back the clock on our brain health.
New research by a team of psychologists uncovered a simple way just about anyone can get their brain working like it’s decades younger.
You probably don’t need science to tell you this, but people’s cognitive acuity generally starts to level off in their 30s and 40s before declining more markedly in their 60s. Most of us write our slower responses and memory lapses off to the unavoidable indignities of aging. But what if they were just the adult equivalent of the “summer slide” that affects kids, a pair of researchers wanted to know.
Sep 25, 2023
9 Benefits of Yoga
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
If you’ve done your “downward dog” yoga pose today, you’re probably feeling more relaxed. Regardless of your level of yoga expertise, if you’re practicing regularly, you can feel better from head to toe. Yoga offers physical and mental health benefits for people of all ages. And, if you’re going through an illness, recovering from surgery or living with a chronic condition, yoga can become an integral part of your treatment and potentially hasten healing. A yoga therapist can work with patients and put together individualized plans that work together with their medical and surgical therapies. That way, yoga can support the healing process and help the person experience symptoms with more centeredness and less distress.
-Aside from these, Yoga also is beneficial to people dealing with Parkinson’s disease. First off it reduces tremors, and it also improves the steadiness of the gait of people with Parkinson’s.
Learn what a Johns Hopkins expert and yoga researcher knows about the benefits and how to get started simply.
Sep 24, 2023
Controlling Devices with Thought, No Open Brain Surgery Required
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, computing, neuroscience
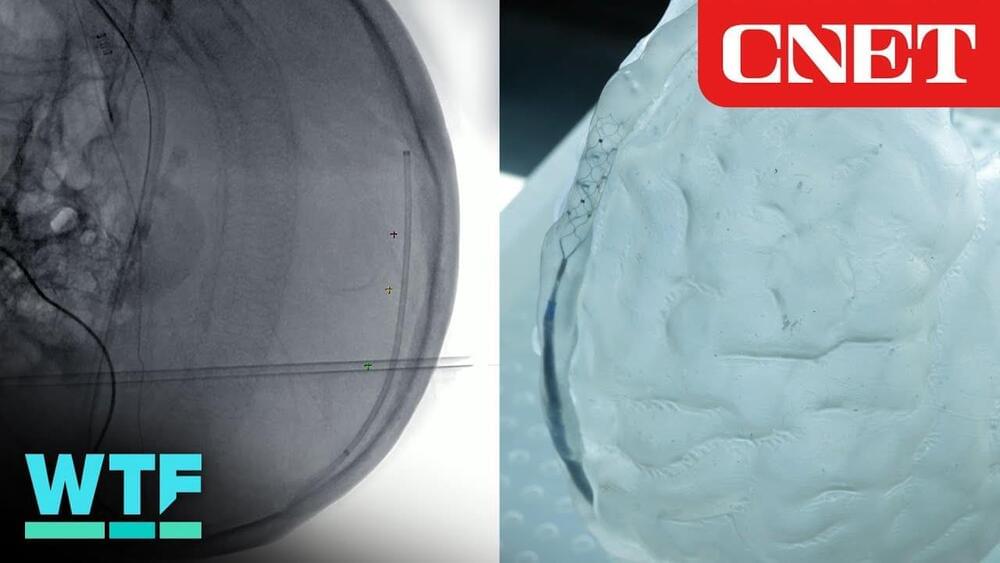
Synchron has developed a Brain-Computer Interface that uses pre-existing technologies such as the stent and catheter to allow insertion into the brain without the need for open brain surgery.
Never miss a deal again! See CNET’s browser extension 👉 https://bit.ly/3lO7sOU
Check out CNET’s Amazon Storefront: https://www.amazon.com/shop/cnet?tag=lifeboatfound-20.
Follow us on TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@cnetdotcom.
Follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/cnet/
Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/cnet.
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/cnet.
#WhatTheFuture #Synchron #BCI
Sep 24, 2023
Molecule reduces inflammation in Alzheimer’s models
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, life extension, neuroscience
Though drug developers have achieved some progress in treating Alzheimer’s disease with medicines that reduce amyloid-beta protein, other problems of the disease, including inflammation, continue unchecked. In a new study, scientists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT describe a candidate drug that in human cell cultures and Alzheimer’s mouse models reduced inflammation and improved memory.
The target of the new “A11” molecule is a genetic transcription factor called PU.1. Prior research has shown that amid Alzheimer’s disease, PU.1 becomes an overzealous director of inflammatory gene expression in the brain’s microglia immune cells. A11 suppresses this problematic PU.1 activity, the new research shows, by recruiting other proteins that repress the inflammatory genes PU.1 works to express. But because A11 concentrates mostly in the brain and does not reduce PU.1 levels, it does not appear to disrupt PU.1’s other job, which is to ensure the production of a wide variety of blood cells.
“Inflammation is a major component of Alzheimer’s disease pathology that has been especially hard to treat,” says study senior author Li-Huei Tsai, Picower Professor of Neuroscience at MIT and director of The Picower Institute and MIT’s Aging Brain Initiative. “This preclinical study demonstrates that A11 reduces inflammation in human microglia-like cells, as well as in multiple mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease, and significantly improves cognition in the mice. We believe A11 therefore merits further development and testing.”