By Joseph Flaherty — Wired
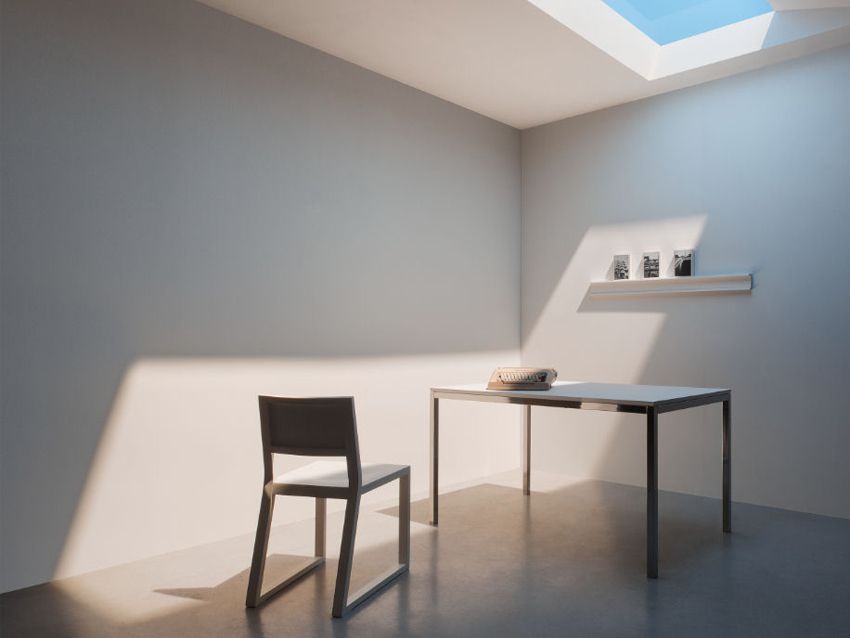

As portions of the US are battered by snowstorms and shrouded beneath gray skies, a European startup is developing a light fixture that mimics the sun.
Each CoeLux fixture models the sunlight of a specific locale, be it the cool color and strong shadows of equatorial countries, the even glow of Mediterranean sunlight, or the slightly dimmer and warmer, but more striking patterns found along the Arctic Circle.
CoeLux fixtures use traditional LEDs, calibrated to the same wavelengths as the sun. However, accurately recreating sunlight also requires mimicking subtle variations caused by the atmosphere, which varies in thickness and composition depending upon where you are on earth. CoeLux uses a milimeters-thick layer of plastic, peppered with nanoparticles, that does essentially the same thing in your living room. CoeLux’s inventor, Professor Paolo Di Trapani hasn’t made any disclosures about how the nanotechnology works in practice, but an impressive list of peer-reviewed publications, industry awards, and testimonials from customers provide comfort that these devices actually work as advertised.
Read more