Oct 9, 2020
Nanoscale machines convert light into work
Posted by Raphael Ramos in categories: chemistry, nanotechnology, particle physics
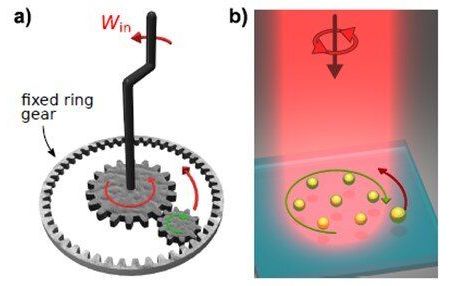
“In previous work, the researchers discovered that when optical matter is exposed to circularly polarized light, it rotates as a rigid body in the direction opposite the polarization rotation. In other words, when the incident light rotates one way the optical matter array responds by spinning the other. This is a manifestation of “negative torque”. The researchers speculated that a machine could be developed based on this new phenomenon.
In the new work, the researchers created an optical matter machine that operates much like a mechanical machine based on interlocking gears. In such machines, when one gear is turned, a smaller interlocking gear will spin in the opposite direction. The optical matter machine uses circularly polarized light from a laser to create a nanoparticle array that acts like the larger gear by spinning in the optical field. This “optical matter gear” converts the circularly polarized light into orbital, or angular, momentum that influences a nearby probe particle to orbit the nanoparticle array (the gear) in the opposite direction.”
Researchers have developed a tiny new machine that converts laser light into work. These optically powered machines self-assemble and could be used for nanoscale manipulation of tiny cargo for applications such as nanofluidics and particle sorting.
Continue reading “Nanoscale machines convert light into work” »