Jan 21, 2023
Quiet, ultrathin AirJet solid state active cooling chips could replace fans
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: computing, mobile phones
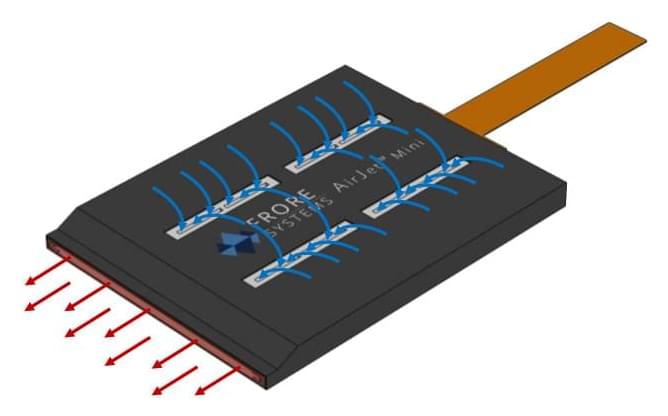
Frore Systems Airjet Mini and Airjet Pro are active cooling chips that are just 2.8mm thick and quietly suck cool air in from the top of the chip before pushing it out the sides with the aim to replace traditional fan-based solutions in ultrabooks, or be integrated into VR headsets and smartphones for improved cooling.
Yesterday we saw that cameras could clean themselves with micro-vibrations, and it happens that processors can be cooled with vibrations too as the Airjet chips are comprised of tiny membranes that vibrate at ultrasonic frequencies to generate a flow of air that enters through inlet vents in the top and transformed into high-velocity pulsating jets exiting from one side of the chip.