To capture a broader understanding of memory encoding, we expanded our experiments to include two other stimulus types: colors and face pictures (see Materials and Methods). Both monkeys demonstrated high accuracy in memorizing grating orientations in the “orientation DMTS” task, colors in the “color DMTS” task, and face pictures in the “face DMTS” task [DP: ~94% and DQ: ~87% versus 50%, all P < 0.01 (one-sample t test)] (fig. S1), indicating that they had been well trained.
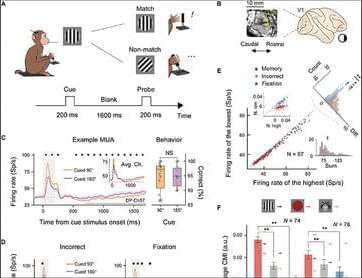
We implanted a Utah array in each monkey’s V1 area (see Materials and Methods; Fig. 1B) and presented the stimuli onto the receptive field (RF) centers of the recorded neurons (fig. S2, A and D). This enabled simultaneous monitoring of neuronal activity in our experiments. Our analyses focused primarily on neuronal activity before probe stimulus onset.
Representative neuronal responses for two of the VWM content conditions in the orientation DMTS task at a selected electrode are shown in Fig. 1C. During the stimulus period (0 to 200 ms after cue onset), neurons displayed distinct firing patterns between the two content conditions (90° or 180° orientation). An off-response emerged following the cue offset, and activity gradually diminished. During the delay period, defined as 700 to 1,700 ms after cue onset (the thick gray line in Fig. 1C), neurons also exhibited a significant difference in firing rate between the two content conditions (N = 1,810 trials for 90°; N = 1,865 trials for 180°; all marked positions P < 0.01) without any behavioral performance bias (N = 16 sessions, P = 0.94; right panel in Fig. 1C). The difference in response between these two content conditions during the delay period at the same electrode was less prominent in incorrect-response trials and in the fixation task (Fig. 1D).