Jan 26, 2016
New algorithm points the way towards regrowing limbs and organs
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biotech/medical, computing, information science, neuroscience
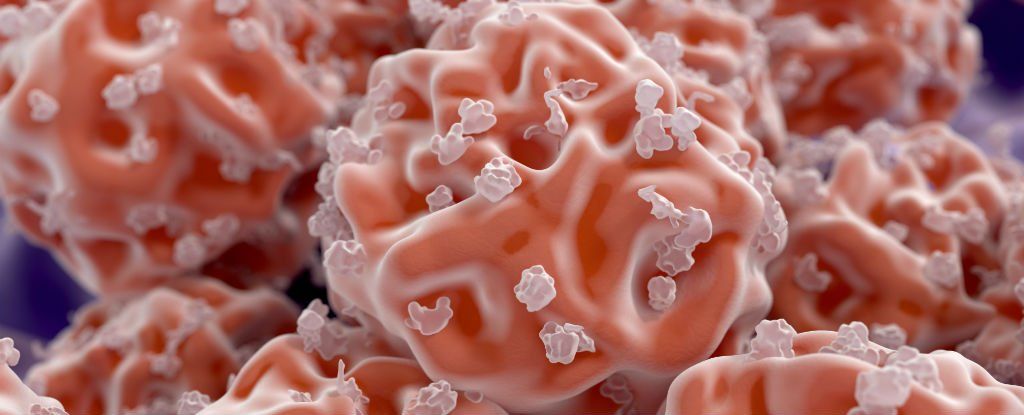
An international team of researchers has developed a new algorithm that could one day help scientists reprogram cells to plug any kind of gap in the human body. The computer code model, called Mogrify, is designed to make the process of creating pluripotent stem cells much quicker and more straightforward than ever before.
A pluripotent stem cell is one that has the potential to become any type of specialised cell in the body: eye tissue, or a neural cell, or cells to build a heart. In theory, that would open up the potential for doctors to regrow limbs, make organs to order, and patch up the human body in all kinds of ways that aren’t currently possible.
It was Japanese researcher Shinya Yamanaka who first reprogrammed cells in this way back in 2007 — it later earned him a Nobel Prize — but Yamanaka’s work involved a lot of labourious trial and error, and the process he followed is not an easy one to reproduce. Mogrify aims to compute the required set of factors to change cells instead, and it’s passed its early tests with flying colours.






 Deep Learning in Action | A talk by Juergen Schmidhuber, PhD at the Deep Learning in Action talk series in October 2015. He is professor in computer science at the Dalle Molle Institute for Artificial Intelligence Research, part of the University of Applied Sciences and Arts of Southern Switzerland.
Deep Learning in Action | A talk by Juergen Schmidhuber, PhD at the Deep Learning in Action talk series in October 2015. He is professor in computer science at the Dalle Molle Institute for Artificial Intelligence Research, part of the University of Applied Sciences and Arts of Southern Switzerland.








