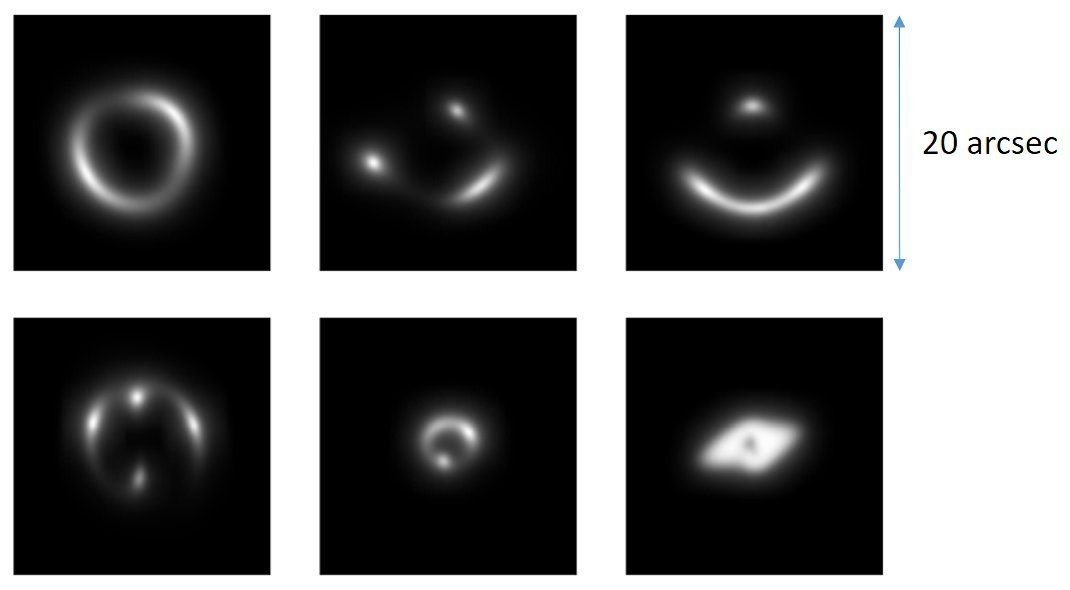
A group of astronomers from the universities of Groningen, Naples and Bonn has developed a method that finds gravitational lenses in enormous piles of observations. The method is based on the same artificial intelligence algorithm that Google, Facebook and Tesla have been using in the last years. The researchers published their method and 56 new gravitational lens candidates in the November issue of Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
When a galaxy is hidden behind another galaxy, we can sometimes see the hidden one around the front system. This phenomenon is called a gravitational lens, because it emerges from Einstein’s general relativity theory which says that mass can bend light. Astronomers search for gravitational lenses because they help in the research of dark matter.
The hunt for gravitational lenses is painstaking. Astronomers have to sort thousands of images. They are assisted by enthusiastic volunteers around the world. So far, the search was more or less in line with the availability of new images. But thanks to new observations with special telescopes that reflect large sections of the sky, millions of images are added. Humans cannot keep up with that pace.
Continue reading “Artificial intelligence finds 56 new gravitational lens candidates” »