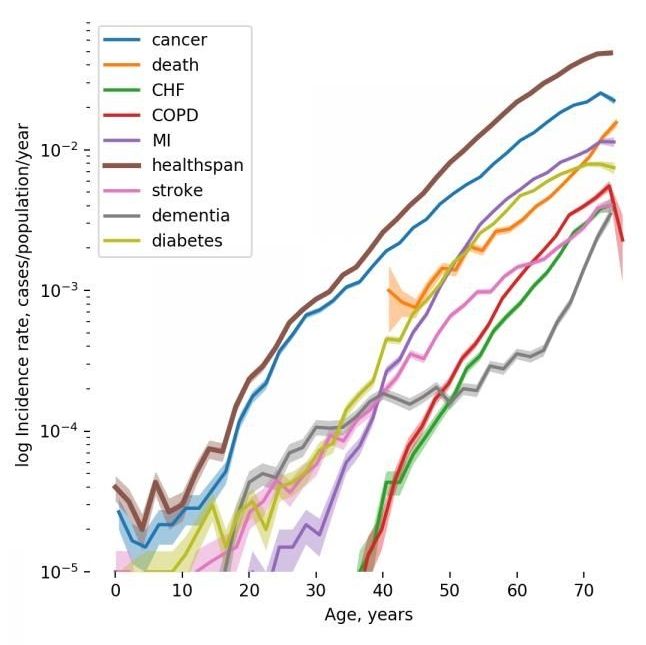
The global population aged 60 or over is growing faster than all younger age groups and faces the tide of chronic diseases threatening their quality of life and posing challenges to healthcare and economy systems. To better understand the underlying biology behind healthspan — the healthy period of life before the first chronic disease manifestation — the scientists from Gero and MIPT collaborated with the researchers from PolyOmica, the University of Edinburgh and other institutes to analyze genetic data and medical histories of over 300,000 people aged 37 to 73 made available by UK Biobank.
The study published today in Communications Biology was lead by Dr. Peter Fedichev and Prof. Yurii Aulchenko. It shows that the most prevalent chronic conditions such as cancer, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, dementia, and some others apparently share the common underlying mechanism that is aging itself.
«According to Gompertz mortality law, the risk of death from all causes increases exponentially after the age of 40 and doubles approximately every 8 years», explains Peter Fedichev, founder and CSO of Gero. «By analyzing the dynamics of disease incidence in the clinical data available from UKB, we observed that the risks of age-related diseases grow exponentially with age and double at a rate compatible with the Gompertz mortality law. This close relation between the most prevalent chronic diseases and mortality suggests that their risks could be driven by the same process, that is aging. This is why healthspan can be used as a natural proxy for investigation of the genetic factors controlling the rate of aging, the “holy grail” target for anti-aging interventions».
Read more