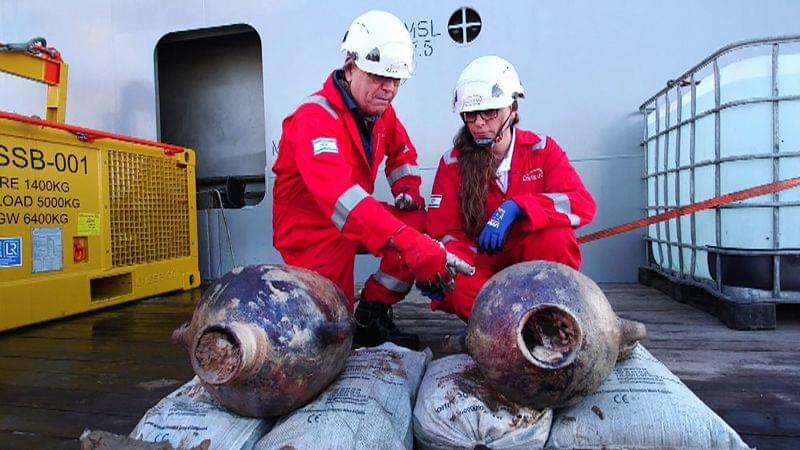
A 3,300-year-old ship has been discovered at the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea, making it one of the oldest shipwrecks ever discovered and rewriting our understanding of sailing in the ancient world, according to the Israel Antiquities Authority.
The vessel is estimated to be from the 13th or 14th century BCE, the authority said in a statement. It was discovered 90 kilometers (around 56 miles) from the shore, in waters 1.8 kilometers (1.1 miles) deep, with hundreds of intact jars still on board, the statement added.
The ship’s remains were found during an environmental survey of the seabed by London-based natural gas production company Energean, according to Karnit Bahartan, the head of the company’s environment team.