Aug 21, 2022
Old Bones Carry Evidence of Why Ancient Empires Collapsed
Posted by Len Rosen in categories: biotech/medical, food
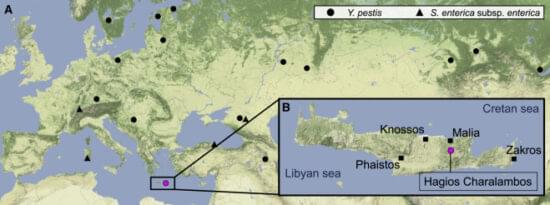
Burial sites in the Eastern Mediterranean from the period around 2000 BCE show evidence of outbreaks of disease that likely contributed to the fall of three great civilizations: the Minoan on the island of Crete, the Akkadian in what is Turkey today, and Egypt’s Old Kingdom.
The pathogens found in the DNA of old bones indicate significant outbreaks of typhoid fever and the plague. The emergence of widespread disease in this area of the world at that time may be related to climate change, or pressures from new waves of human migration coming from outside the region. But a paper published in Current Biology on July 25, 2022, shows widespread infections involving the bacterium Yersinia pestis, responsible for the many incidents of plague that occurred in ancient civilizations all the way to the era of Justinian 1st in the 6th century CE Eastern Roman Empire which modern scholars labelled Byzantine. Also found in burial sites is widespread evidence of Salmonella Enterica the cause of typhoid/enteric fever.
This evidence coincides with a period of major geopolitical transformation from 2,290 to 1909 BCE. During this time the Old Kingdom, the Akkadian Empire, and the Middle Minoan civilization were all disrupted. The periods are associated with societal and population declines throughout much of the Eastern Mediterranean. Did these depopulating diseases come from elsewhere brought in by migration and invasion? Were there environmental factors such as a change in the climate? Was there degradation of agricultural lands leading to famine, and a general weakening of the local population?