Mar 30, 2024
Study demonstrates atomic layer deposition route to scalable, electronic-grade van der Waals tellurium thin films
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: engineering, particle physics
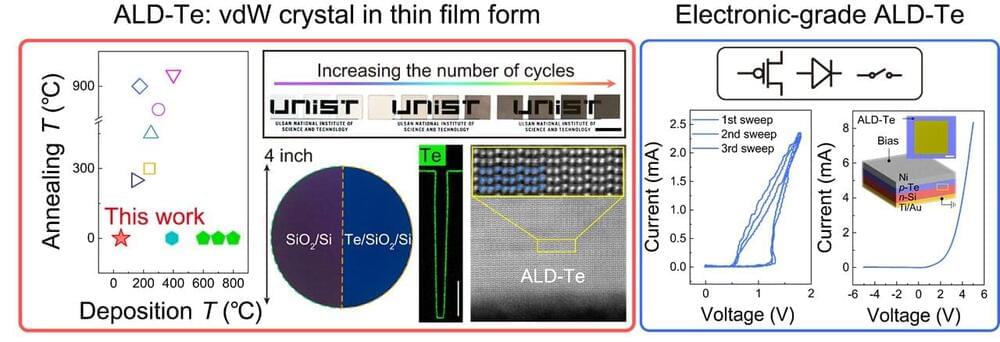
A research team, led by Professor Joonki Suh in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and the Graduate School of Semiconductor Materials and Devices Engineering at UNIST, has made a significant breakthrough in thin film deposition technology. By employing an innovative atomic layer deposition (ALD) process, Professor Seo successfully achieved regular arrangement of tellurium (Te) atoms at low temperatures as low as 50 degrees Celsius.
The ALD method is a cutting-edge thin film process that enables precise stacking of semiconductor materials at the atomic layer level on three-dimensional structures—even at low process temperatures. However, traditional application to next-generation semiconductors requires high processing temperatures above 250 degrees Celsius and additional heat treatment exceeding 450 degrees Celsius.
In this research, the UNIST team applied ALD to monoelemental van der Waals tellurium—a material under extensive investigation for its potential applications in electronic devices and thermoelectric materials.