Archive for the ‘energy’ category: Page 297
Aug 8, 2018
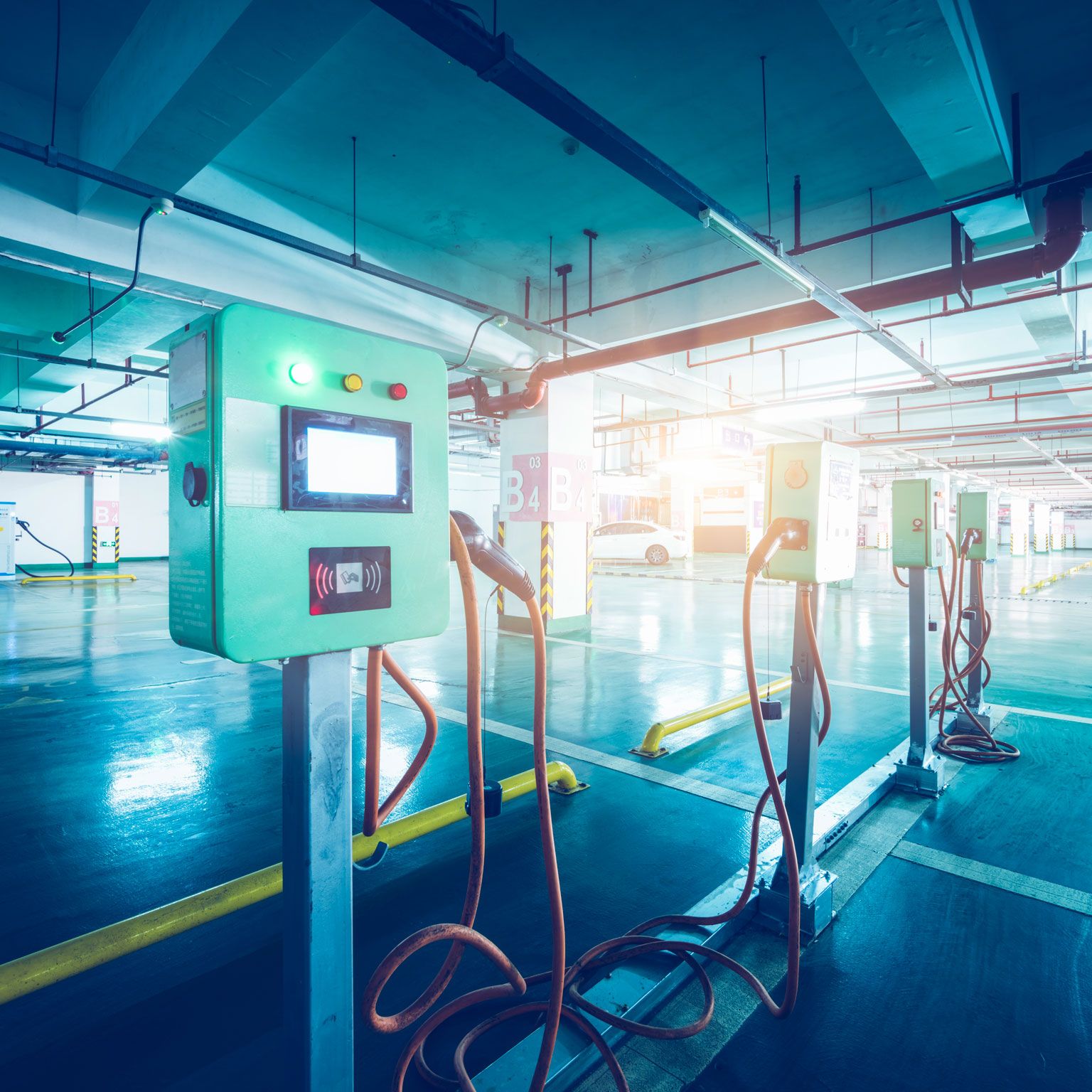
The potential impact of electric vehicles on global energy systems
Posted by Bill Kemp in categories: energy, transportation
Electric vehicles are unlikely to create a power-demand crisis but could reshape the load curve. Here’s how to bend that curve to your advantage.
Could electric vehicles (EVs) soon face a different kind of gridlock? With the electrification of mobility accelerating, energy producers and distributors need to understand the potential impact of EVs on electricity demand (Exhibit 1). The good news: McKinsey analysis suggests the projected growth in e-mobility will not drive substantial increases in total electrical-grid power demand in the near to midterm, thus limiting the need for new electricity-generation capacity during that period.
Aug 8, 2018
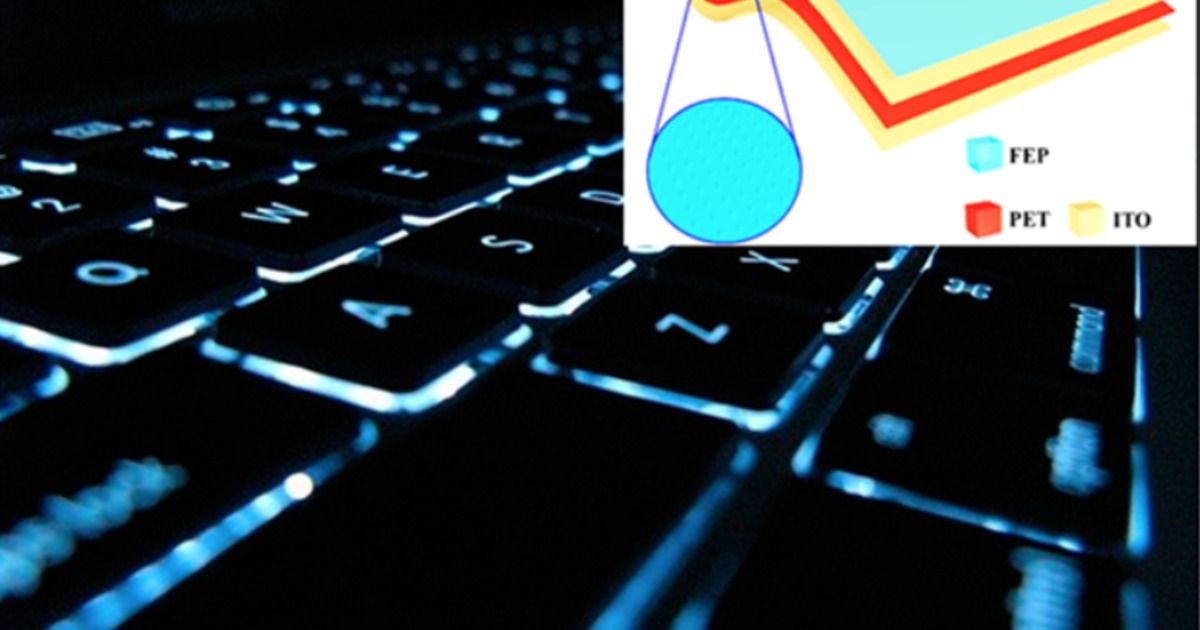
Smart Keyboard Could Be Self-Powered, Self-Secured, Self-Cleaning
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: energy
Scientists have come up with a prototype keyboard that can recognize different typing styles, provide its own power, and possibly even keep itself clean.
Aug 8, 2018
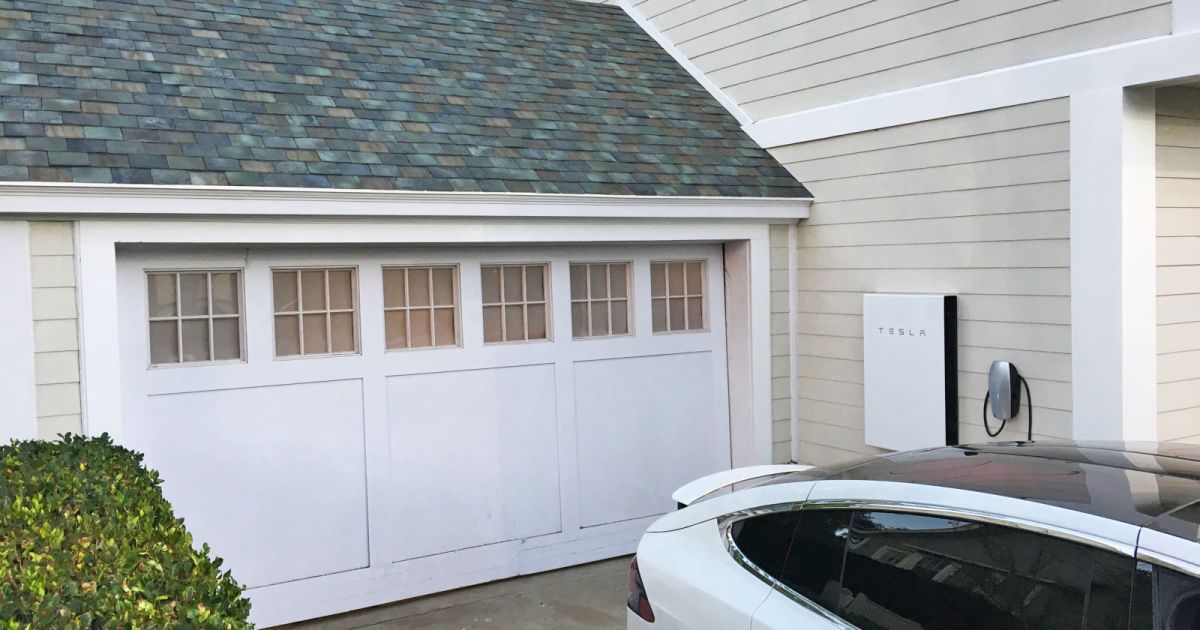
Tesla’s production problems extend to its solar roof business, too
Posted by Bill Kemp in categories: business, Elon Musk, energy, sustainability, transportation
The production problems Tesla has faced with its Model 3 have been well documented. Now, sources say the company is facing similar issues with its solar roof tile initiative. According to Reuters, former and current employees have revealed that assembly line problems, plus CEO Elon Musk’s exacting aesthetic demands, has delayed production, causing tension with partner Panasonic, and rattling officials that are keen to see a return on significant state investment.
The “Solar Roof,” produced at Tesla’s factory in Buffalo, New York, is designed to look like and function as a regular roof while also generating energy. According to sources, technical challenges have delayed production, as has Musk’s design plans. Speaking to Reuters, one source said that “Aesthetic look is the key point that Elon is not always satisfied with. That’s the big issue.”
Neither Tesla nor Reuters’ sources have revealed current production figures for the roof tiles, but the delays are such that Panasonic — which the initiative depends on for solar components — has been forced to find other buyers for the parts it had built to sell to Tesla. According to a former Panasonic employee, the company has been shipping “large volumes” of its photovoltaic cells as samples to other prospective buyers, due to low demand from Tesla. Panasonic declined to comment on the issue, stating only that it “believes Tesla will use Panasonic cells when it mass-markets the Solar roof.”
Continue reading “Tesla’s production problems extend to its solar roof business, too” »
Aug 4, 2018
Scientists Discover the Great Pyramid of Giza’s Design Can Concentrate Electromagnetic Energy
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: energy, physics
Researchers from St Petersburg’s ITMO University in Russia and Laser Zentrum Hannover in Germany have discovered a fascinating phenomenon regarding the design of the Great Pyramid of Giza.
A theoretical investigation published in the Journal of Applied Physics on July 20 2018 reveals the chambers within the Great Pyramid can “collect and concentrate electromagnetic energy.” Scientists looked at the “excitation of the pyramid’s electromagnetic dipole and quadrupole moments,” or the combinations of outgoing and incoming electromagnetic waves, to determine its capacity for electromagnetic focus. Using numerical simulations to deduce their findings, the research team found that under certain conditions, the pyramid’s internal chambers and the area under its base (where the third, unfinished chamber is located) can concentrate this energy.
Modern physics has provided unprecedented insight into the secrets of the pyramids, which were constructed around 2560 BC. For instance, cosmic ray-based imaging (also known as muon tomography) has been used to see further into the depths of these ancient structures, illuminating a previously unknown “large void” that humans haven’t encountered in several millennia.
Aug 4, 2018
This Is What Happens When Bitcoin Miners Take Over Your Town
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: bitcoin, energy
Eastern Washington had cheap power and tons of space. Then the suitcases of cash started arriving.
Aug 2, 2018
In China, flame-throwing drones are often used to clear debris off power lines
Posted by Mary Jain in categories: drones, energy
Jul 31, 2018
Coordinated ocean energy efforts herald a new industrial sector
Posted by Bill Kemp in categories: energy, sustainability
Despite its remaining mystery, the ocean is a complex working environment, widely used for fishing, shipping and recreation; but so far largely untapped for energy generation. OCEANERA-NET seeks to give the industry the boost it needs.
The European Union coastline runs to around 66 000 kilometres. This vast stretch holds a largely unexploited potential for ocean generated electricity, calculated to be around 380 GW by DG MARE (the EU Directorate responsible), constituting a significant contribution to the EU’s 2020 targets for renewable energy.
Presently, there are a number of Member States funding research and development into ocean energy technology. However, these efforts are not coordinated and so not the game-changers they could be.
Continue reading “Coordinated ocean energy efforts herald a new industrial sector” »
Jul 30, 2018
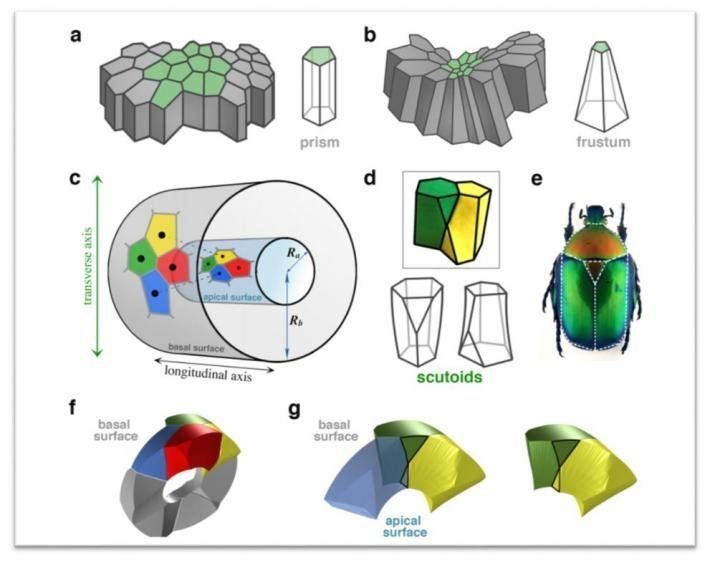
New geometric shape used by nature to pack cells efficiently
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: energy
These cells pack together tightly. To accommodate the curving that occurs during embryonic development, it has been assumed that epithelial cells adopt either columnar or bottle-like shapes.
However, a group of scientists dug deeper into this phenomenon and discovered a new geometric shape in the process.
They uncovered that, during tissue bending, epithelial cells adopt a previously undescribed shape that enables the cells to minimize energy use and maximize packing stability. The team’s results will be published in Nature Communications in a paper called “Scutoids are a geometrical solution to three-dimensional packing of epithelia.”
Continue reading “New geometric shape used by nature to pack cells efficiently” »
Jul 25, 2018
Nanotech powers this super-sensitive microphone
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: energy, nanotechnology
The trouble with microphones is that they don’t just hear — they have to listen. Powering the mic and its signal processor means using energy, and energy means a battery, and a battery means charging. This new microphone-like system hears more like the way our own ears do, requiring little or no power, and could help fill the world with voice-responsive machines. (If that’s something we really want.)
The device is called a “triboelectric auditory sensor,” and it works via what’s called the triboelectric effect — essentially when two surfaces rub together and create a charge. They’re still trying to figure out why this happens, but what matters to engineers is that it happens reliably.
Triboelectric nanogenerators have been around for a few years, creating power by having two compatible materials interact with each other at super-small scales. While they’re tiny and highly efficient, they don’t actually produce a lot of power. Researchers from Chongqing University found that, fortunately, you don’t need a lot of power for the purposes of detecting sound.
Continue reading “Nanotech powers this super-sensitive microphone” »