Mar 8, 2021
SN4KE: A lightweight and scalable framework for binary mutation testing
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in category: cybercrime/malcode
When developers deliver software to their clients, they often also provide what is known as a ‘test suite.’ A test suite is a tool that allows users to test software, unveil any bugs it might have and give developers a chance to fix these bugs or other potential issues.
In addition to evaluating software, therefore, developers also need to ascertain the efficacy of a test suite in identifying bugs and errors. One way to run test suite evaluations is via mutation testing, a technique that generates several ‘mutants’ of a program by slightly modifying its original code. While mutation testing tools have proved to be incredibly helpful, most of them cannot be applied to software that is only available in binary code (a way of representing texts or instructions for computers using two symbols, generally ‘0’ and ‘1’).
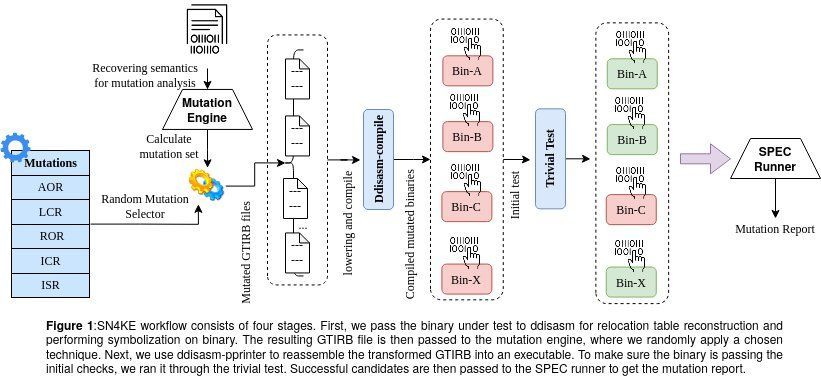
Researchers at Arizona State University, Worcester Polytechnic Institute and the University of Minnesota have recently developed SN4KE, a framework that can be used to carry out mutation analyses at a binary level. This framework, presented at the Binary Analysis Research (BAR) NDSS symposium ‘21 in February, is a new tool to efficiently test suites for software based on binary codes.