Feb 20, 2023
The enigmatic black behemoths that govern our galaxy
Posted by Dan Breeden in category: cosmology
Scientists try to unravel the birth, growth and power of black holes, some of the most forceful yet difficult-to-detect objects in our universe.
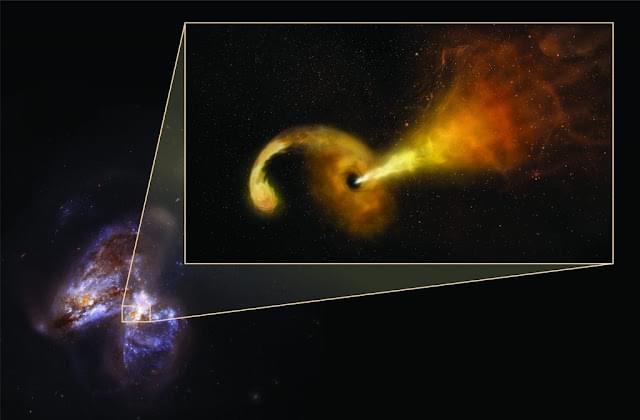
It was only last year that astronomers were finally able to unveil the first pictures of the supermassive black hole at the center of our Milky Way galaxy. But you couldn’t actually see the black hole itself, not directly. That’s because it is so dense that its gravitational pull prevents even light from escaping.
But the image of Sagittarius A, as our galaxy’s black hole is known, revealed a glowing halo of gas around the object—an object that we now know has a million times more mass than our sun.