Jul 12, 2016
A New Design Strategy for Better Lithium Oxygen Batteries
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: chemistry, computing, transportation
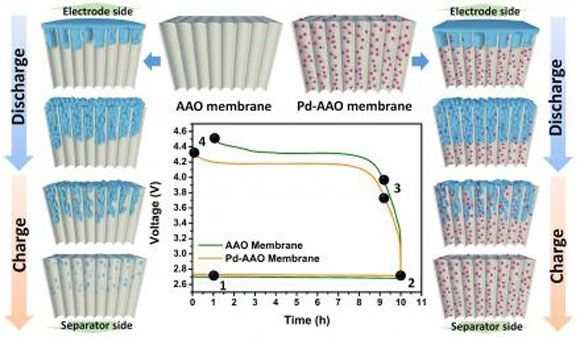
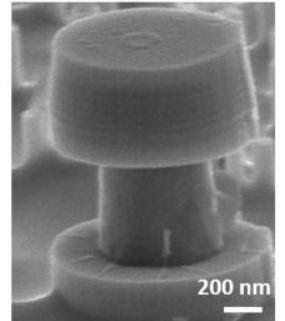
Yale researchers have devised a method that brings marketable Li-O2 batteries closer to reality, improving both the batteries’ performance and the ability to study them.
In recent years, lithium-oxygen batteries have intrigued researchers with their potential. They can store at least two to three times the energy as lithium-ion batteries can, which are the current standard for consumer electronics, so laptops could theoretically run longer on a single charge and electric cars would drive farther.
But they’re not quite there yet. For now, Li-O2 batteries operate sluggishly and have short lives. Compounding matters, it’s hard to get a sense of how to fix that because figuring out the exact nature of their chemistry has proved tricky.
Continue reading “A New Design Strategy for Better Lithium Oxygen Batteries” »