Archive for the ‘computing’ category: Page 748
Sep 5, 2016
AI Lawyer “Ross” Has Been Hired By Its First Official Law Firm
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: computing, law, robotics/AI

https://youtube.com/watch?v=Y_cqBP08yuA
Ross, the world’s first artificially intelligent attorney, has its first official law firm. Baker & Hostetler announced that they will be employing Ross for its bankruptcy practice, currently comprised of almost 50 lawyers.
Law firm Baker & Hostetler has announced that they are employing IBM’s AI Ross to handle their bankruptcy practice, which at the moment consists of nearly 50 lawyers. According to CEO and co-founder Andrew Arruda, other firms have also signed licenses with Ross, and they will also be making announcements shortly.
Continue reading “AI Lawyer ‘Ross’ Has Been Hired By Its First Official Law Firm” »
Sep 5, 2016
Quantum computing Rose’s Law is Moore’s Law on steroids
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, quantum physics

https://youtube.com/watch?v=6VIAL8gQRTI
Rose’s Law for Quantum Computing highlights the new platforms sheer power to solve humanity’s and society’s most complex problems on, and off, Earth
When Steve Jurvetson, Managing Director of the investment firm Draper Fisher Jurvetson (DJF) first met Geordie Rose, now CTO and former CEO of D-Wave back in 2002 he was struck by his ability to explain complex quantum physics and the “spooky” underpinnings of a new class of computing platform – Quantum Computing.
Continue reading “Quantum computing Rose’s Law is Moore’s Law on steroids” »
Sep 5, 2016
A Look at IBM’s Watson 5 Years After Its Breathtaking Jeopardy Debut
Posted by Elmar Arunov in categories: biotech/medical, computing, robotics/AI
The year was 2012, and IBM’s AI software Watson was in the midst of its heyday.
Watson beat two of Jeopardy’s all-time champions a year earlier in 2011, and the world was stunned. It was the first widespread and successful demonstration of a natural language processing computer of its class. Combined with the popularity of Jeopardy, Watson became an immediate mainstream icon.
Later in 2012, IBM announced one of the first major practical partnerships for Watson—a Cleveland Clinic collaboration to bring the system into medical training.
Continue reading “A Look at IBM’s Watson 5 Years After Its Breathtaking Jeopardy Debut” »
Sep 5, 2016
Artificial intelligence wants to be your bro, not your foe
Posted by Elmar Arunov in categories: computing, economics, education, employment, policy, robotics/AI, surveillance, transportation
The odds that artificial intelligence will enslave or eliminate humankind within the next decade or so are thankfully slim. So concludes a major report from Stanford University on the social and economic implications of artificial intelligence.
At the same time, however, the report concludes that AI looks certain to upend huge aspects of everyday life, from employment and education to transportation and entertainment. More than 20 leaders in the fields of AI, computer science, and robotics coauthored the report. The analysis is significant because the public alarm over the impact of AI threatens to shape public policy and corporate decisions.
It predicts that automated trucks, flying vehicles, and personal robots will be commonplace by 2030, but cautions that remaining technical obstacles will limit such technologies to certain niches. It also warns that the social and ethical implications of advances in AI, such as the potential for unemployment in certain areas and likely erosions of privacy driven by new forms of surveillance and data mining, will need to be open to discussion and debate.
Continue reading “Artificial intelligence wants to be your bro, not your foe” »
Sep 4, 2016
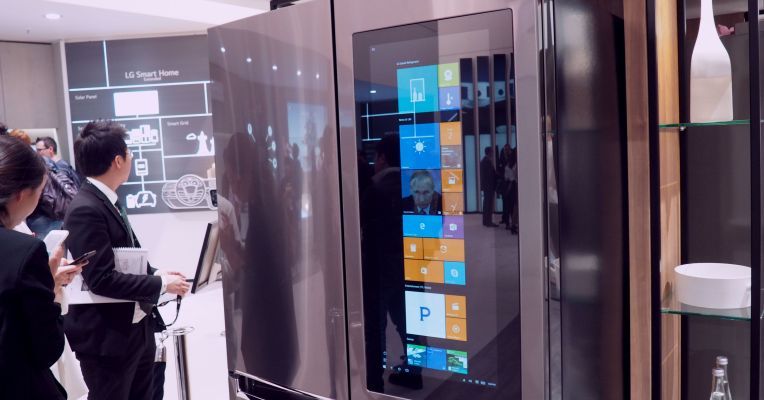
Finally, Windows 10 on a refrigerator door
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: computing
To the thousands, nay, millions who were holding out for a Windows 10 fridge before upgrading, we’ve got some pretty great news straight from the IFA show floor. Granted, it’s still just a prototype with no firm release date, but here you go. LG put a fully functioning Windows 10 tablet on the door of a fancy new icebox.
And it’s a massive tablet, at that – measuring 27 inches, powered by an Intel Atom processor located up top. It actually seems to work pretty well, in the demo we got on the showroom floor. It’s surprisingly responsive – a lot more than many of the sorts of displays companies jam onto their appliances in the name of smartness.
What is the meaning of affective computing? Are machines able to feel? Find out more about this new concept in this analysis from Ahmed Banafa for OpenMind.
Sep 3, 2016
Neuromorphic Chips: a Path Towards Human-level AI
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, neuroscience, robotics/AI
[Figure about depicts a layout, showing two ‘somas’, or circuits that simulate the basic functions of a neuron. The green circles play the role of synapses. From presentation of K.K. Likharev, used with permission.]
One possible layout is shown above. Electronic devices called ‘somas’ play the role of the neuron’s cell body, which is to add up the inputs and fire an output. In neuromorphic hardware, somas may mimic neurons with several different levels of sophistication, depending on what is required for the task at hand. For instance, somas may generate spikes (sequences of pulses) just like neurons in the brain. There is growing evidence that sequences of spikes in the brain carry more information than just the average firing rate alone, which previously had been considered the most important quantity. Spikes are carried through the two types of neural wires, axons and dendrites, which are represented by the red and blue lines in figure 2. The green circles are connections between these wires that play the role of synapses. Each of these ‘latching switches’ must be able to hold a ‘weight’, which is encoded in either a variable capacitance or variable resistance. In principle, memristors would be an ideal component here, if one could be developed that could be mass produced. Crucially, all of the crossnet architecture can be implemented in traditional silicon-based (“CMOS”-like) technology. Each crossnet (as shown in the figure) is designed so they can be stacked, with additional wires connecting somas on different layers. In this way, neuromorphic crossnet technology can achieve component densities that rival the human brain.
Likarev’s design is still theoretical, but there are already several neuromorphic chips in production, such as IBM’s TrueNorth chip, which features spiking neurons, and Qualcomm’s “Zeroeth” project. NVIDIA is currently making major investments in deep learning hardware, and the next generation of NVIDIA devices dedicated for deep learning will likely look closer to neuromorphic chips than traditional GPUs. Another important player is the startup Nervana systems, which was recently acquired by Intel for $400 million. Many governments are are investing large amounts of money into academic research on neuromorphic chips as well. Prominent examples include the EU’s BrainScaleS project, the UK’s SpiNNaker project, and DARPA’s SyNAPSE program.
Continue reading “Neuromorphic Chips: a Path Towards Human-level AI” »
Sep 3, 2016
Turing Learning breakthrough: Computers can now learn from pure observation
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, innovation
Soon, the machines really might be watching your every move — and, for the first time, independently making sense of what they see.
Sep 3, 2016
The World’s First 1000-Core Processor Was Just Created
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, encryption
UC Davis has developed the KiloCore, a CPU that has 1000 cores suited for parallel tasks like encryption, crunching scientific data, and encoding videos.
Processor technology has certainly come far, with a host of different materials and techniques being implemented to increase speed and power. And now, we have a new kind of development. A team of scientists at UC Davis made the world’s first 1000-core processor.
The team has unveiled the KiloCore, a CPU that has 1000 cores and all the speed that come with that kind of power. The chip has a maximum computation rate of 1.78 trillion instructions per second and contains 621 million transistors.
Continue reading “The World’s First 1000-Core Processor Was Just Created” »