Oct 20, 2016
Bendable WhammyPhone offers flexible music control
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: computing, media & arts, mobile phones
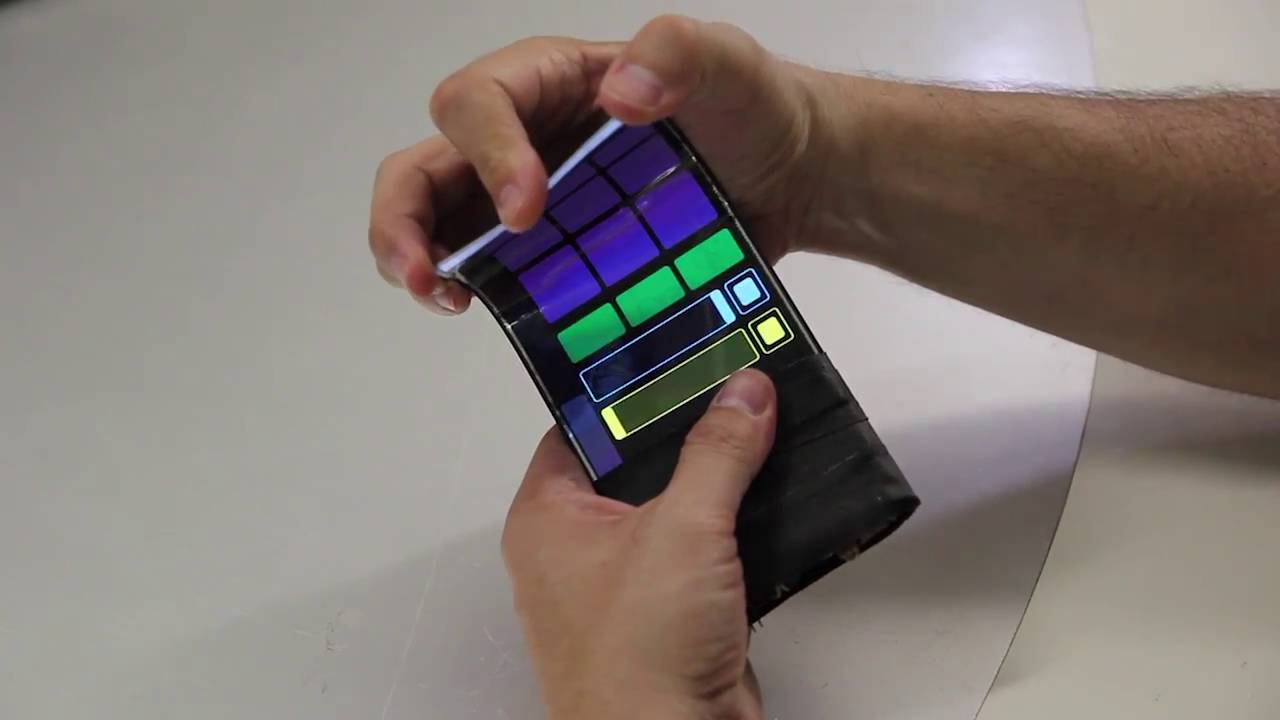
Earlier this year, a team from Queen’s University in Canada demonstrated a smartphone prototype called ReFlex that had a flexible display capable of flipping virtual book pages in response to what were dubbed bend gestures. Researchers from the same Human Media Lab have now developed a similar device called the WhammyPhone that’s claimed to be the world’s first virtual musical instrument for flexible phones.
The WhammyPhone prototype sports a 1920 × 1080 pixel full high-definition Flexible Organic Light Emitting Diode (FOLED) touchscreen display and, like the ReFlex device, includes a bend sensor. This means that a user can manipulate the sound of electronically-generated instruments such as a guitar or violin by bending, squeezing or twisting the “smartphone.”
Continue reading “Bendable WhammyPhone offers flexible music control” »