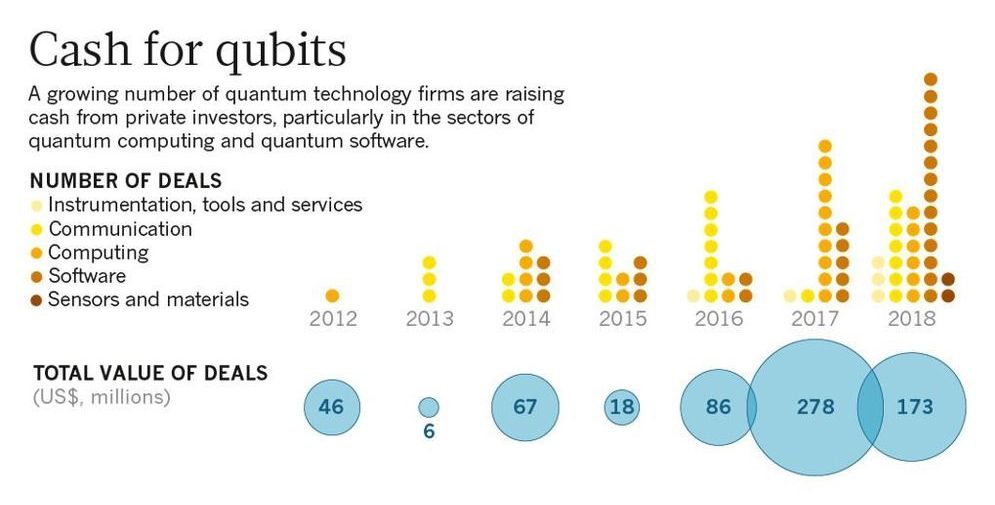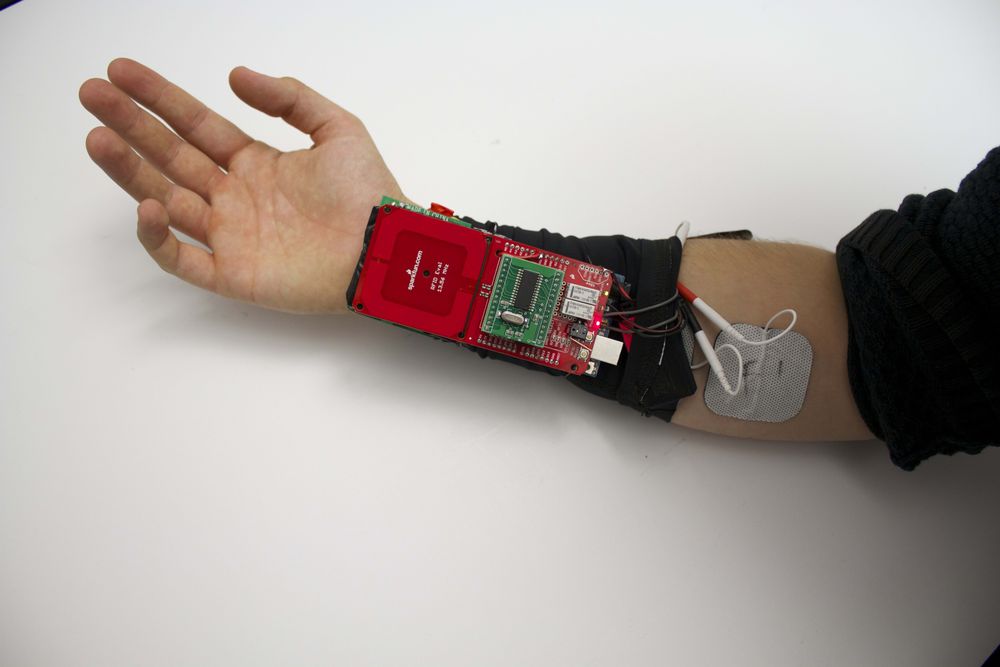
A professor at the University of Chicago believes he is on his way to creating a wearable for market that will manipulate your muscles with electrical impulses to cause you to move involuntarily so you can perform a physical task you otherwise didn’t know how to do, like playing a musical instrument or operating machinery.
Dr. Pedro Lopes, who heads the Human Computer Integration lab at the university, is all about integrating humans and computers, closing the gap between human and machine. His team, which focuses on engineering the next generation of wearable and haptic devices, is exploring the endless possibilities if wearables could intentionally share parts of our body for input and output, allowing computers to be more directly interwoven in our bodily senses and actuators.
Lopes’ vision: a wearable EMS device that would look like a sleeve and be able to send electrical impulses in the right timing and in the right fashion to make a user’s muscles move involuntarily to perform a physical task. EMS stands for electrical muscle stimulation.