Jun 4, 2020
Arrays of strontium Rydberg atoms show promise for use in quantum computers
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: computing, particle physics, quantum physics
A team of researchers at California Institute of Technology has found that arrays of strontium Rydberg atoms show promise for use in a quantum computer. In their paper published in the journal Nature Physics, the researchers describe their study of quantum entangled alkaline-earth Rydberg atoms arranged in arrays and what they learned about them. In the same issue, Wenhui Li, with the National University of Singapore, has published a News & Views piece exploring the state of quantum computing research, and outlines the work done by the team at CIT.
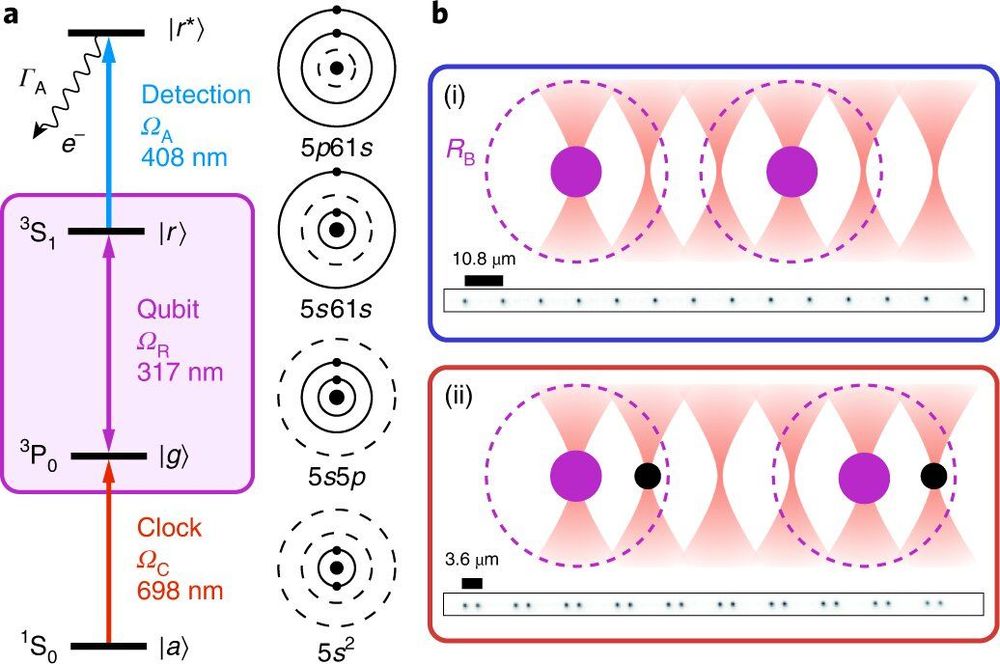
Quantum computers capable of conducting real computing work have still not been realized, but work continues as scientists are confident that the goal will be reached. And as Li notes, most of the early-stage demo quantum computers are based on superconducting qubits or trapped ion platforms, though other systems are being studied, as well. One such system is based on neutral atoms in which the charges of the protons and electrons balance. In this new effort, the researchers looked at a type of neutral atom system based on Rydberg atoms (excited atoms with one or more electrons that also have a high quantum number). To use such atoms in a quantum computer, they must, of course, be entangled—and there needs to be a lot of them, generally arranged in an array.
In their work, the team at CIT developed a way to demonstrate entanglement of Rydberg atoms in arrays—and as part of the system, they were able to detect and control Rydberg qubits with unprecedented fidelities. To achieve this feat, they began with realizing photon coupling between different levels of Rydberg ground-state qubits, thus avoiding scattering. Doing so also allowed for efficient detection of Rydberg states, greatly improving detection fidelity. The researchers also demonstrated two-qubit entanglement using tweezer potentials, also with high fidelity.