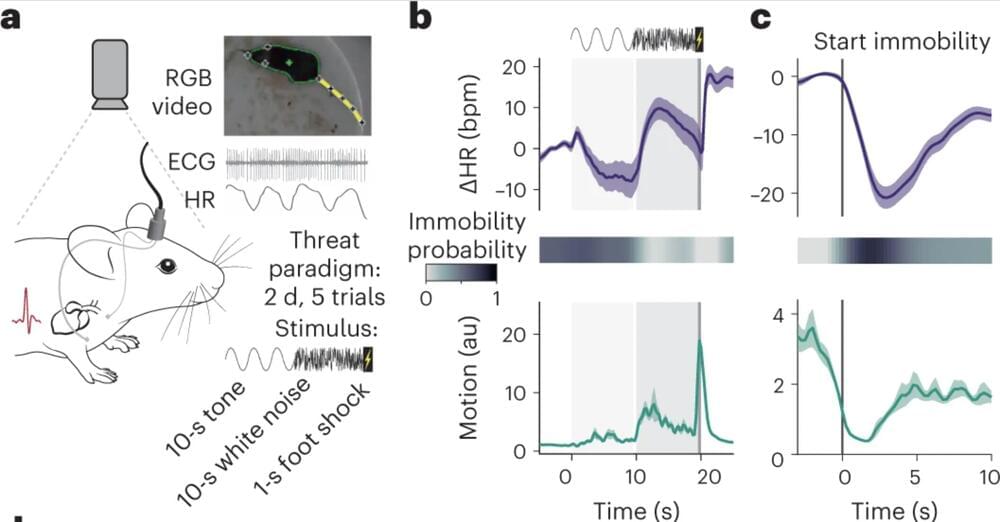
Anxiety disorders are becoming increasingly common, with estimates suggesting that almost one in three people in the U.S. will experience high levels of anxiety at some point in their life. Anxiety is essentially a feeling of unease, worry or psychological discomfort, typically associated with catastrophic thoughts about a real or imagined future life event.
When they are anxious, humans experience the same sensations and physiological responses they would feel when they are afraid of a real and immediate threat, such as a lion chasing them, an ongoing natural disaster, and so on. To better support patients with anxiety disorders, neuroscientists and psychology researchers have been trying to understand the neural underpinnings of fear and anxiety for many years.
Ultimately, both fear and anxiety tend to promote defensive behaviors in response to real or imaginary threats, respectively. The most widely documented among these are the so-called freeze (i.e., staying still), flight (i.e., avoiding a feared situation or escaping), fight (i.e., arguing or becoming aggressive) and fawn (i.e., overpleasing or submitting to another human to avoid the escalation of conflict).