Apr 4, 2023
Genetic analysis tool developed to improve cancer modeling
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, genetics, health
Lifestyle behaviors such as eating well and exercising can be significant factors in one’s overall health. But the risk of developing cancer is predominantly at the whim of an individual’s genetics.
Our bodies are constantly making copies of our genes to produce new cells. However, there are occasional mistakes in those copies, a phenomenon geneticists call mutation. In some cases, these mistakes can alter proteins, fuse genes and change how much a gene gets copied, ultimately impacting a person’s risk of developing cancer. Scientists can better understand the impact of mutations by developing predictive models for tumor activity.
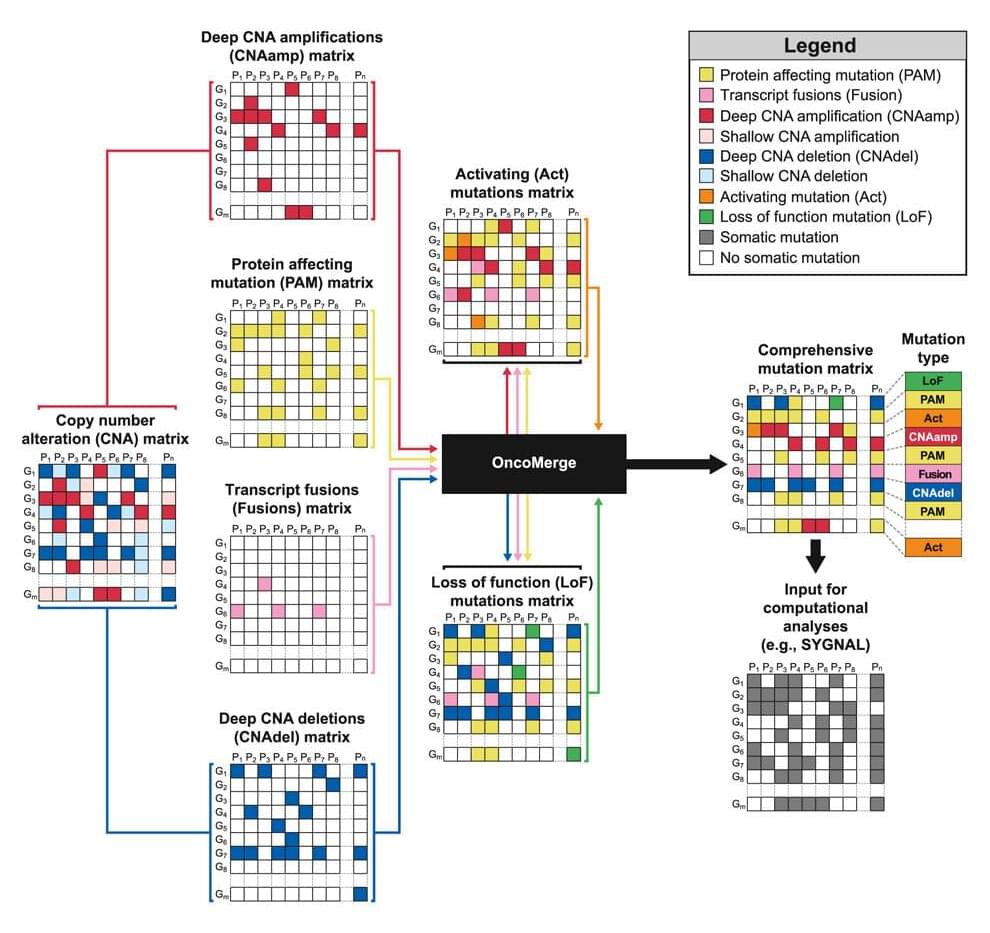
Christopher Plaisier, an assistant professor of biomedical engineering in the Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering at Arizona State University, is developing a software tool called OncoMerge that uses genetic data to improve cancer modeling technology.