Nov 13, 2024
When muscles work out, they help neurons grow: Biochemical and physical effects of exercise could help heal nerves
Posted by Cecile G. Tamura in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, health, neuroscience
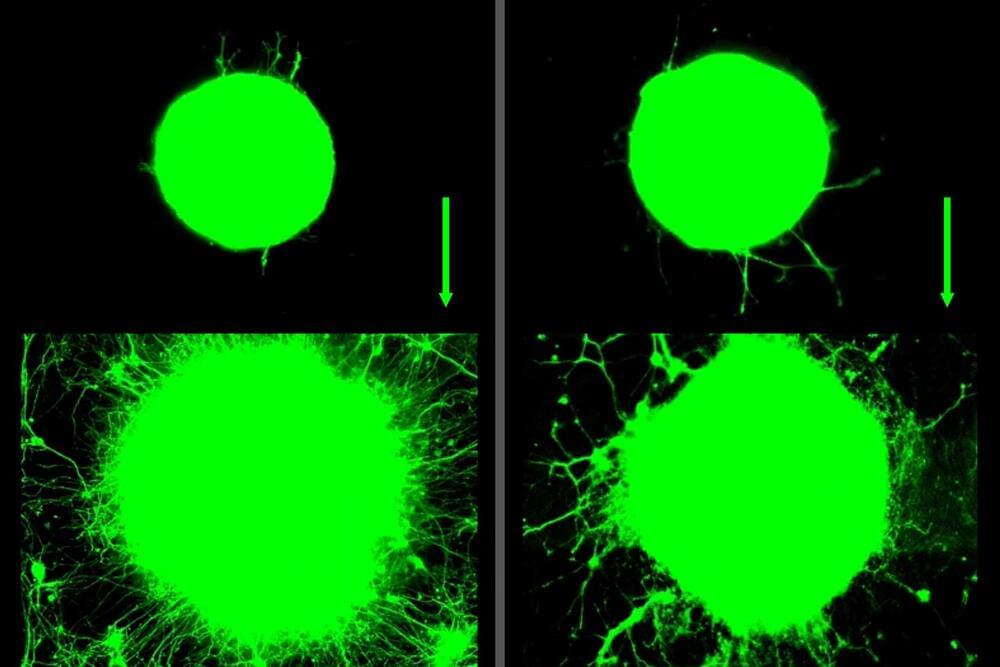
This study explores how muscle contractions, such as those that occur during exercise, influence motor neurons—the cells responsible for controlling muscle movement.
There’s no doubt that exercise does a body good. Regular activity not only strengthens muscles but can bolster our bones, blood vessels, and immune system.
Now, MIT engineers have found that exercise can also have benefits at the level of individual neurons. They observed that when muscles contract during exercise, they release a soup of biochemical signals called myokines.