Aug 8, 2015
Scientists reveal secrets for reaching age 100 (or more)
Posted by Sean Brazell in categories: biotech/medical, health
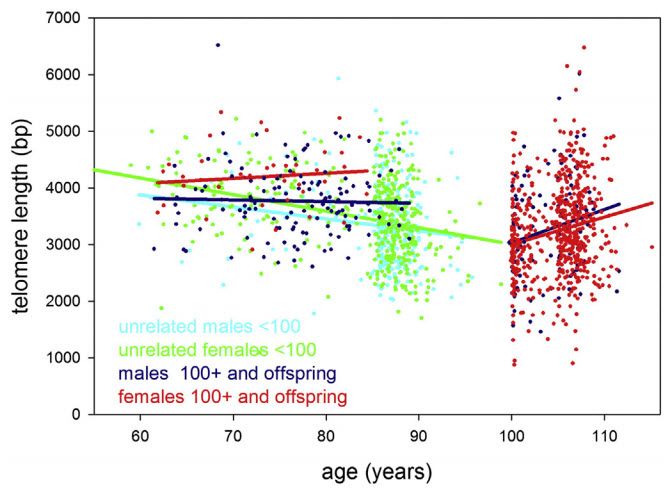
Leukocyte (white blood cell) telomere length in study participants up to 115 years of age. Statistical regression lines belonging to these groups are indicated by the same color as the data. (credit: Yasumichi Arai et al./EBioMedicine)
Scientists say they have cracked the secret of why some people live a healthy and physically independent life over the age of 100: keeping inflammation down and telomeres long.
Newcastle University’s Institute for Ageing in the U.K. and Keio University School of Medicine note that severe inflammation is part of many diseases in the old, such as diabetes or diseases attacking the bones or the body’s joints, and chronic inflammation can develop from any of them.
Continue reading “Scientists reveal secrets for reaching age 100 (or more)” »