Apr 12, 2020
Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China
Posted by Nicholi Avery in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
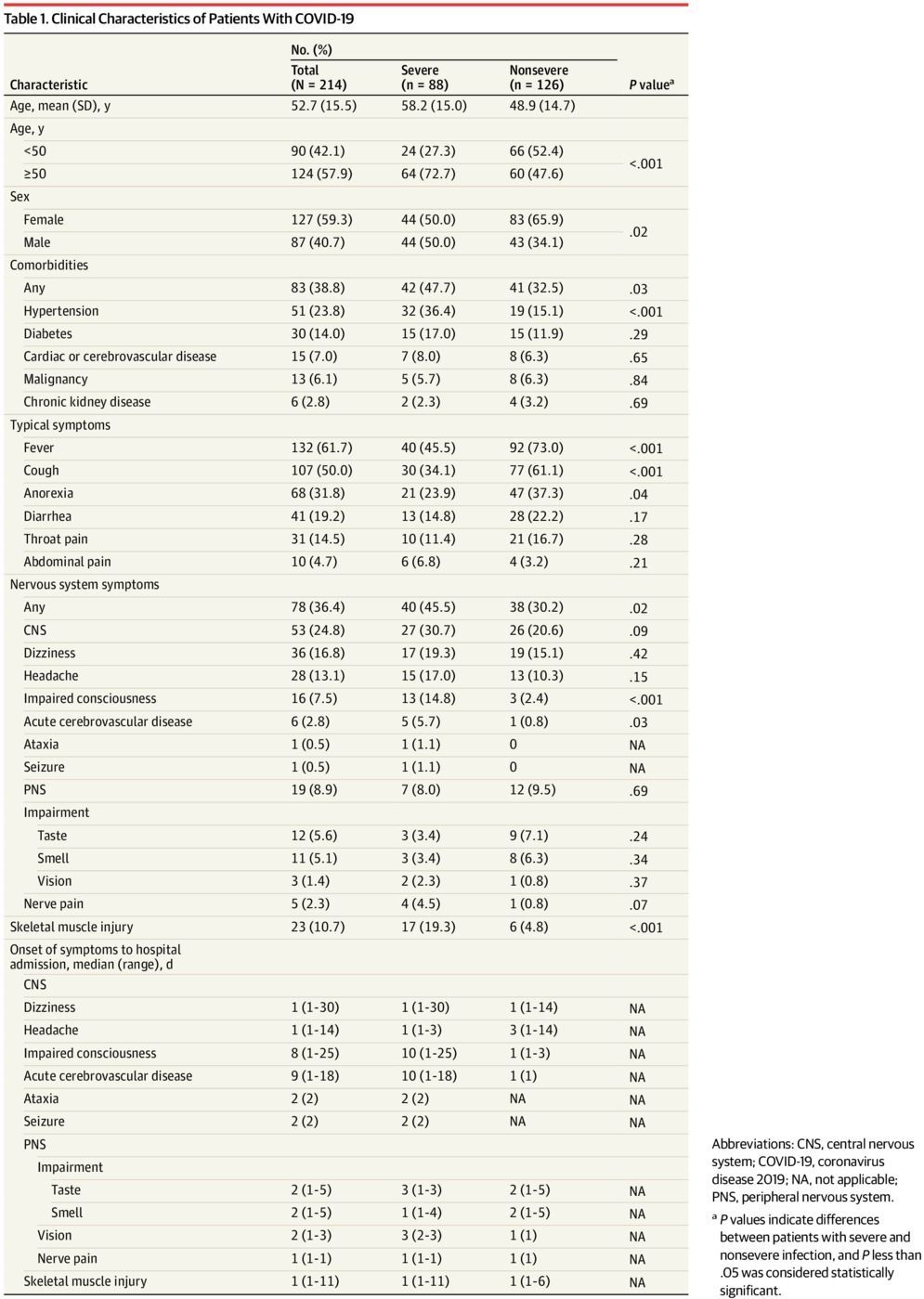
Findings In a case series of 214 patients with coronavirus disease 2019, neurologic symptoms were seen in 36.4% of patients and were more common in patients with severe infection (45.5%) according to their respiratory status, which included acute cerebrovascular events, impaired consciousness, and muscle injury.
Published Online: April 10, 2020. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127
Author Contributions: Dr B. Hu had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Drs Mao, Jin, M. Wang, Y. Hu, Chen, He, and Chang contributed equally and share first authorship.